Vertrieb in Unternehmen ist wie der Motor, der eine Maschine antreibt. Nur wenn Produkte verkauft werden und neue Kunden sich für ein Unternehmen begeistern, kann der nötige Cashflow generiert werden, der Gebäude, Löhne und alle anderen Kosten rund um das Unternehmen tragen kann.
Wie man diesen Bereich eines Unternehmens mit Data Mining und Web Scraping aktiv unterstützen kann, zeige ich euch in diesem Artikel.
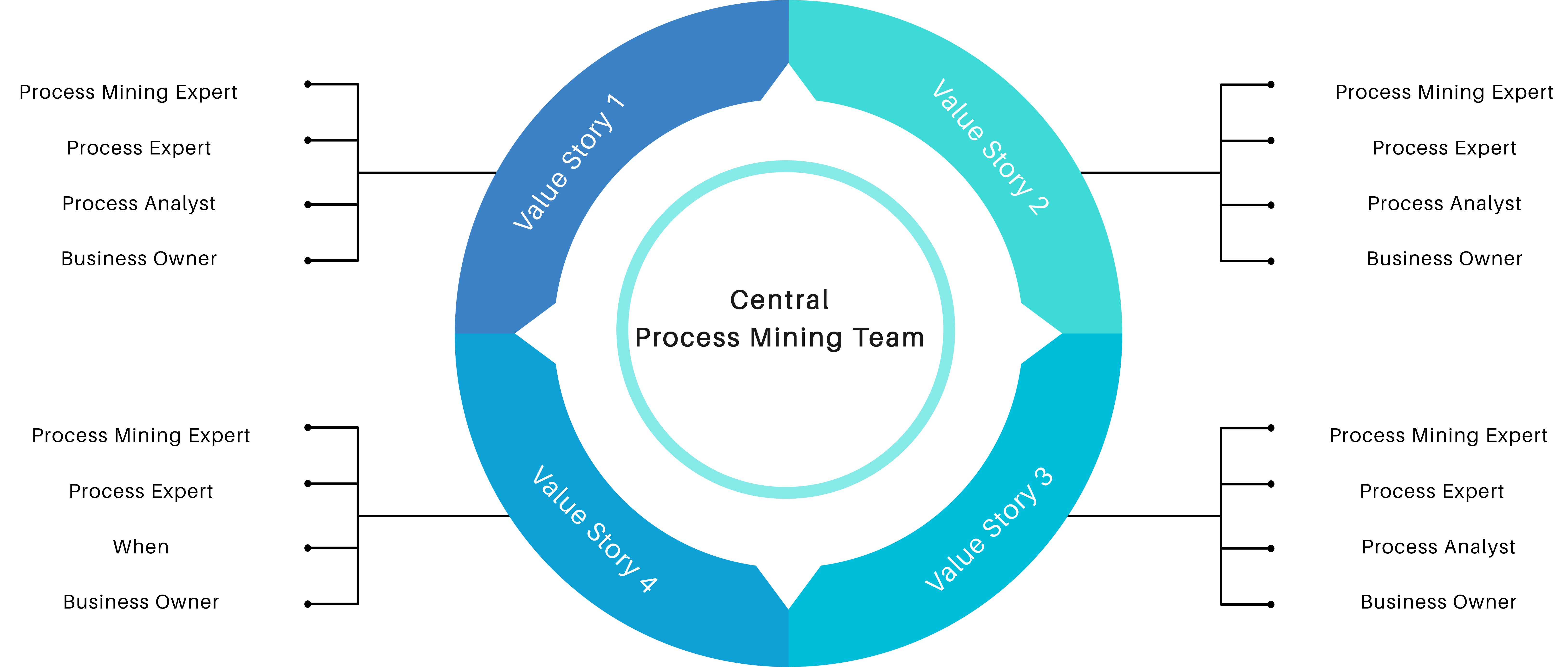
Kernthema im Vertrieb: Leadgenerierung
Jeder Verkauf beginnt mit einer Person, die an unserem Produkt interessiert ist und es kaufen möchte. Ein zentraler Punkt im Vertrieb sind deshalb die “Leads” – Kontaktadresse von Kunden, mit denen wir ins Gespräch kommen können, um ein Angebot zu machen und schließlich unsere Produkte zu verkaufen. Die Leads sind die Basis in jedem Vertriebsprozess, weil wir über diese Daten mit Menschen ins Gespräch kommen können und Beziehungen zu potentiellen Kunden aufbauen können. Je besser diese vorselektiert sind und auf unsere Zielgruppe angepasst sind, desto einfacher wird die Arbeit für unseren Vertrieb.
Leadgenerierung meint dabei das Sammeln von Daten zu Unternehmen oder Personen, die zu unserer Zielgruppe passen und mit möglichst hoher Wahrscheinlichkeit einen Bedarf an unserem Produkt haben. Um in einem Unternehmen einen konstanten Umsatz zu erwirtschaften und die Produktion das ganze Jahr über auszulasten, müssen regelmäßig Aufträge in das Unternehmen kommen. Damit der Vertrieb diese Aufträge an Land ziehen kann, müssen die Vertriebsmitarbeiter immer wieder neue Kundengespräche führen. Und damit diese Gespräche stattfinden können, muss ein Unternehmen auf zuverlässige und wiederholbare Weise immer wieder Leads generieren. Immer wieder neue, potenzielle Interessenten zu finden, ist dabei eine der herausforderndsten Aufgaben jeder Vertriebsleitung.
Leads generieren mit Web Scraping
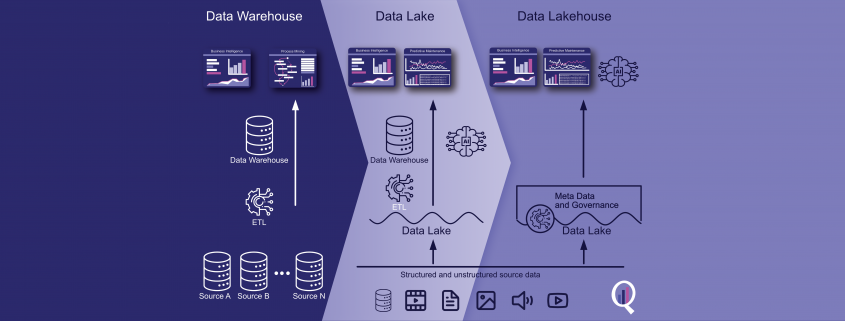
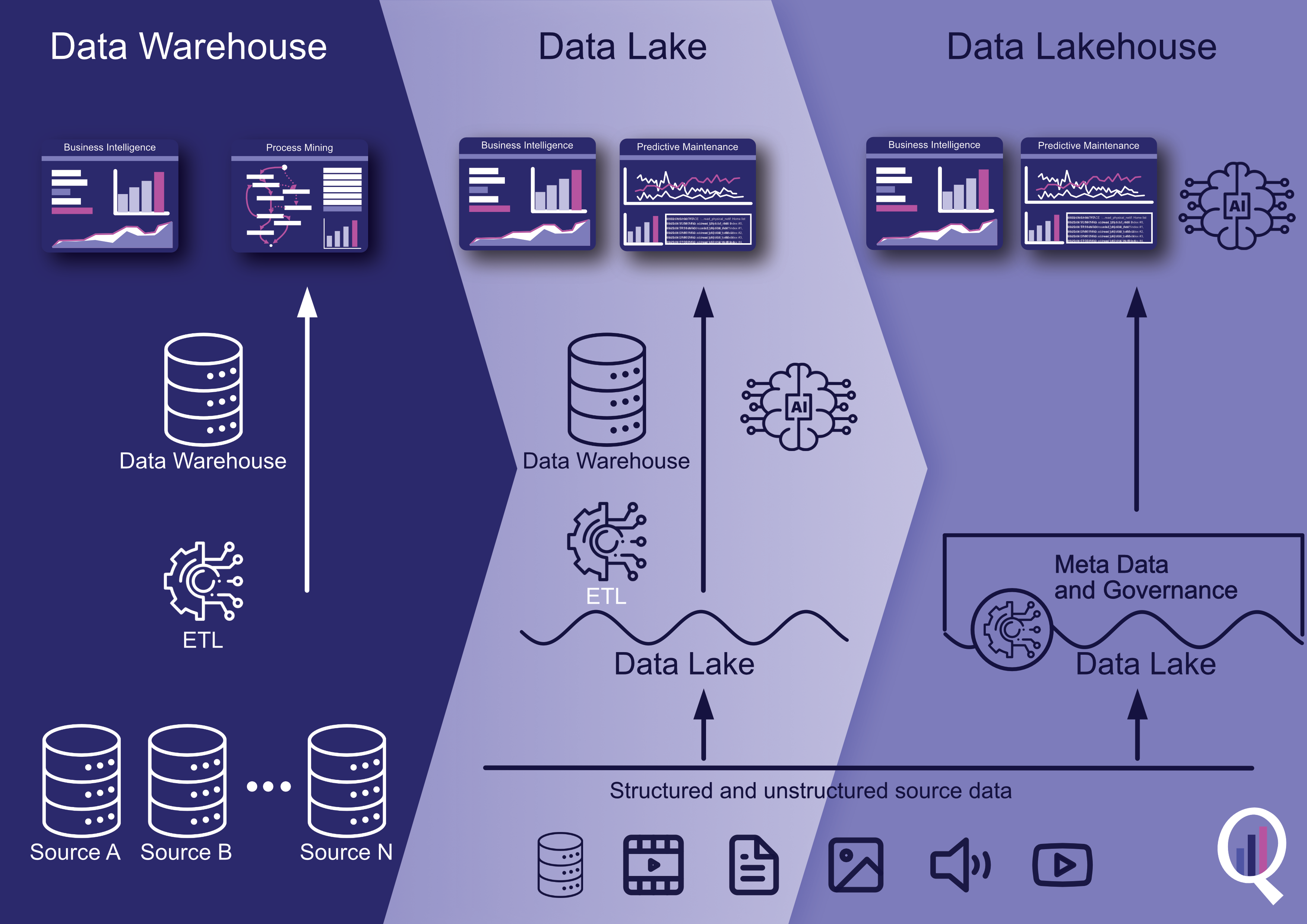
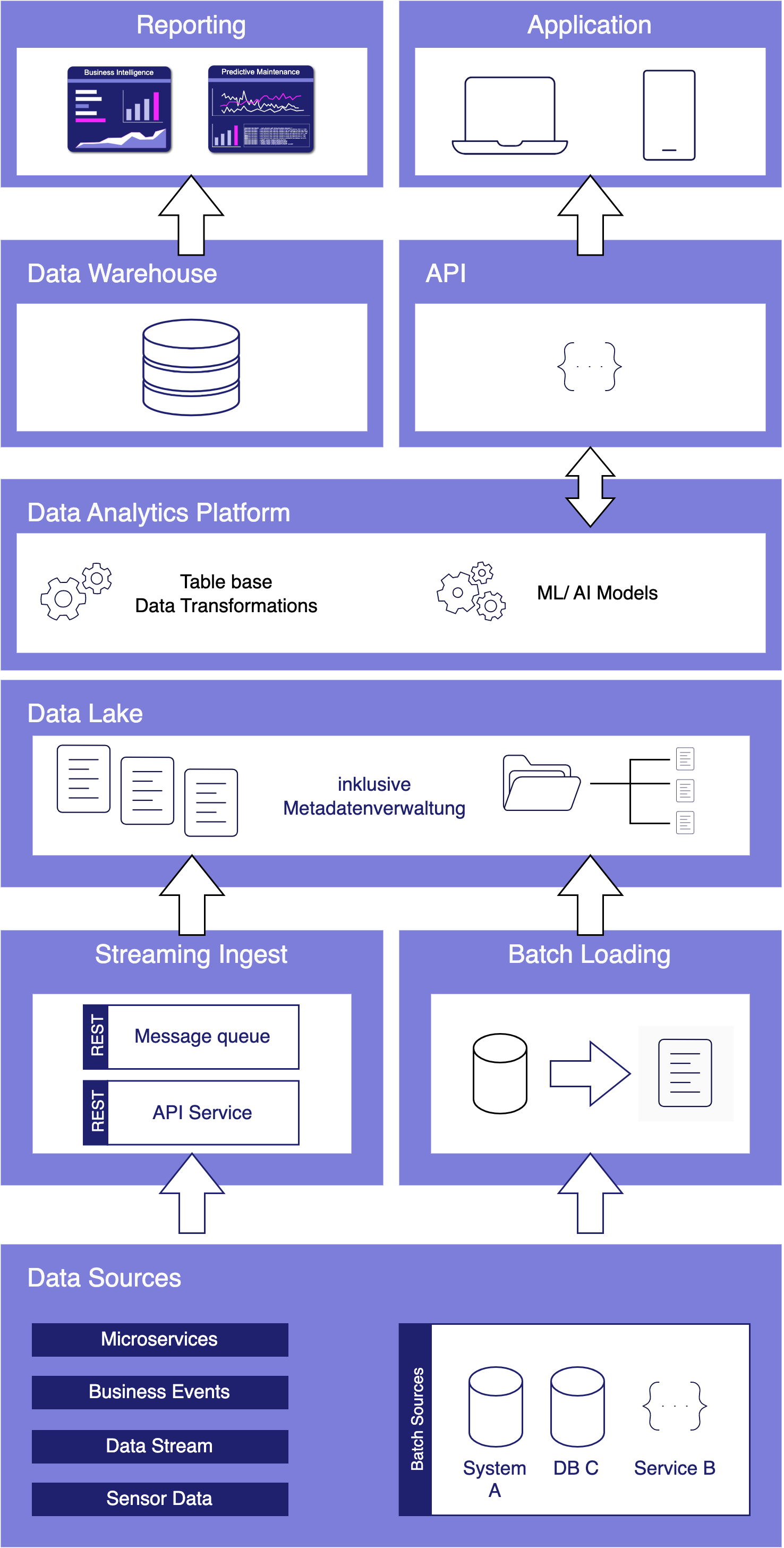
Mit Web Scraping Leads zu generieren bedeutet Kontaktdaten aus dem Internet zu sammeln mit Hilfe einer Software. Vorwiegend werden dabei Webseiten und frei zugängliche Daten aus allen Ecken des Internets durchsucht mit einem Programm, welches anschließend die Daten in eine übersichtliche Datei, wie beispielsweise Excel, verpackt. Dadurch können diese Daten wiederum sehr einfach in die meisten gängigen CRM (Customer Relationship Management) Systeme hochgeladen werden, wo die Vertriebsteams diese direkt bearbeiten können. Mit dieser Methode lassen sich in kurzer Zeit auf die Zielgruppe spezialisierte Listen erstellen, die dem Unternehmen helfen, neue Kundenkontakte zu finden und zu erstellen.
Die Daten dabei können Namen von Personen oder Unternehmen sein, Adressen, Telefonnummern, E-Mail-Adressen, URLs und mehr. Unternehmen und Start-ups ersparen sich damit die mühsame Arbeit dutzende Webseiten und Datenbanken nach möglichen Kontaktadressen zu suchen. Web Scraper sind dabei auch um einiges effizienter als ein manueller Suchvorgang, weil die Programme oft mit komplexen Algorithmen arbeiten, die immer wieder optimiert werden, um bestmögliche Ergebnisse zu erreichen.
Die Vorteile von Web Scraping zur Leadgenerierung
Durch die Automatisierung eines sonst sehr zeitaufwendigen Prozesses werden die Ressourcen im Unternehmen besser eingesetzt. Vor allem Vertriebsmitarbeiter können sich dadurch besser ihrer eigentlichen Aufgabe widmen: Zeit mit Kunden verbringen.
Viele Mitarbeiter im Vertrieb sind auch spezialisiert auf den Umgang mit Menschen und sind möglicherweise etwas unbeholfen, wenn es darum geht, Daten zu sammeln und dabei Tage nur vor dem Bildschirm zu verbringen. Mit Web Scraping wird diese eintönige Tätigkeit aus dem Alltag dieser Mitarbeiter herausgenommen. Die Mitarbeiter können den Tätigkeiten auf die sie spezialisiert sind mehr Zeit widmen, und es müssen auch keine teuren Mitarbeiter mehr abgestellt werden für eine Tätigkeit, die ohnehin maschinell besser gelöst werden kann.
Durch die Analyse von unzähligen Daten beim Web Scraping lassen sich manchmal auch bereits Hypothesen über unsere Zielgruppe überprüfen. Dadurch lernen wir bereits vorab, wie unsere Kunden arbeiten, was für sie relevante Themen sind und wie wir sie am besten ansprechen können. Mit Hilfe dieser Daten können wir wiederum bessere Entscheidungen im Marketing und Vertrieb treffen, basierend auf dem echten Verhalten unserer Kunden anstatt nur auf Vermutungen.
Mit Hilfe der Kombination aus effizientem Ressourceneinsatz sowohl von personeller, zeitlicher als auch monetärer Perspektive und die gleichzeitige Auswertung von Daten über Kunden und deren Verhalten lassen sich langfristige Vorteile für ein Unternehmen erzeugen mit denen man der Konkurrenz einen Schritt voraus ist. Richtig umgesetzt lassen sich damit Geschäftsmöglichkeiten und Umsatzpotenziale lukrieren, noch bevor diese am Markt öffentlich bekannt werden.
Die Herausforderungen beim Web Scraping
Wenn diese Taktik so umwerfend funktioniert, warum macht es dann nicht jeder?
Natürlich gibt es auch beim Web Scraping einige Herausforderungen, die zu beachten sind.
Das offensichtlichste davon ist die Qualität der Daten. Auch das komplexeste Programm kann nur die Daten aus dem Internet filtern, die dort öffentlich zugänglich sind. Dies bedeutet aber auch, dass manches davon nicht mehr aktuell ist, anderes wird irrelevant sein und ein Teil davon als Leads für den Vertrieb gar nicht zu gebrauchen.
Dazu kommen Restriktionen beim Crawlen von Webseiten. Viele Seiten blockieren bewusst Crawler und sind sehr sensibel beim Umgang mit deren Daten, was erneut zu Problemen führen kann. In vielen Fällen müssen diese Seiten ausgeschlossen werden oder sind gar nicht für die Leadgenerierung zu gebrauchen. CAPTCHAs sind dabei nur eine der möglichen Hürden, die den Prozess entweder stark verlangsamen oder völlig stoppen können.
Doch auch selbst wenn Daten frei zugänglich zu finden sind, kommen diese oft mehr als ein Mal vor auf diversen Quellen im Netz. Dies sorgt in den Ergebnissen der Scraper oft für Duplikate. Dabei kann auch der Aufbau einer Webseite Schwierigkeiten bereiten, zumal diese unterschiedlich strukturiert und angeordnet sein können, wodurch eine einheitliche Programmierung für das Scraping schwer zu gestalten ist. Hinzu kommen noch technologische Barrieren, die im Netz verbaut sein können, wie die Nutzung von Javascript, dynamischer Content, oder andere Hindernisse auf den verschiedenen Webseiten.
Geeignete Webseiten oder Plattformen finden
Bevor man mit dem Scraping starten kann, muss man zuerst festlegen, welche Seiten oder Plattformen man überhaupt durchsuchen will. Hier sind einige der Faktoren, die man dabei beachten sollte:
Wo finde ich meine Zielgruppe?
Am besten beginnen wir unsere Suche dort, wo unsere Kunden ohnehin bereits sind, wo sie ihre Freizeit verbringen oder nach Informationen suchen. In B2B Märkten können wir alternativ immer die eigenen Webseiten unserer Kunden durchsuchen.
Wie relevant ist die Seite für mein Produkt?
Es ergibt keinen Sinn Seiten zu crawlen, die nichts mit unseren Produkten zu tun haben und bei denen die Nutzer auch nichts mit unserem Produkt anfangen können. Wer beispielsweise Haarpflegeprodukte verkauft, sollte kein Bauforum durchsuchen.
Wie aktuell ist die Webseite?
Wer Daten auf veralteten Webseiten sucht, wird auch nur veraltete Daten finden. Diese sind meistens kaum bis gar nicht brauchbar für den Vertrieb. Die angegebenen Seiten sollten daher möglichst aktuell sein und die Daten darauf regelmäßig aktualisiert werden.
Rechtliche Abklärung
Manche Seiten verbieten explizit das Benutzen jeglicher Daten zu kommerziellen Zwecken. Dies sollte genau analysiert werden, bevor man Daten von einer Seite extrahiert.
Verfügbarkeit und Qualität der Daten:
Manche Seiten machen es Crawlern bewusst schwer an Daten zu kommen, bei manchen bekommt man keinerlei Informationen mehr ohne Captcha Überprüfung, Opt-In Formular, etc. Auch ein Aufbau der Seite in komplexem HTML Code oder Ähnliches kann Scraping zu einer Herausforderung werden lassen, die einem viel Zeit kostet, anstatt sie zu gewinnen.
Beispiele für Web Scraping
Genug mit der Theorie, sehen wir uns nun ein paar konkrete Beispiele an. Im Idealfall hat man einen Programmierer im Unternehmen zur Verfügung, der gerade keine anderen Projekte verfolgen muss und genug Zeit hat, um einen eigenen Web Scraper zu bauen, zielgerichtet auf die Bedürfnisse des Unternehmens. Dieser kann genau auf die Produkte, rechtlichen Anforderungen und die optimalen Kunden für den Vertrieb programmiert werden. Realistisch gesehen, kommt dieses Szenario nur äußerst selten vor. Deshalb stellen wir euch hier einige vorgefertigte Lösungen vor. Die richtige Lösung wird sich bei jedem Unternehmen nach Produkten, Marktlage, Kundenverhalten etc. unterscheiden und muss individuell an jedes Unternehmen angepasst sein.
io
Am Beginn des Vertriebsprozesses brauchen wir eine große Anzahl an Leads. Import.io ist genau einer der Anbieter, die dabei helfen können, große Mengen an Daten aus dem Internet zu erzeugen. Wichtig dabei ist, dass unser restlicher Vertriebsprozess soweit fortgeschritten sein muss, dass wir genau unsere Zielgruppe kennen und wissen, wo und wie man diese Personen finden kann.
Das praktische an dieser Plattform ist, dass man absolut nichts coden oder programmieren muss. Übrigens ist Import.io ursprünglich nicht für Vertriebs- und Marketingzwecke entworfen worden, wird aber immer wieder von gewieften Sales Managern und Marketern als Geheimtipp genutzt. Die Technologie eignet sich hervorragend, um große Listen an Leads mit Web Scraping zu erzeugen.
Die Daten können als .csv Datei gesammelt und von dort optimal in das CRM System der Wahl integriert werden.
Scrape-it Marktplatz
Wer Kundendaten vorwiegend über öffentliche Seiten wie Yellow Pages, Booking.com oder Google Maps finden kann, hat hier ein breites Angebot an verschiedenen Scraper zur Auswahl. Alle davon erfordern keinerlei Programmierung und sind bereit zum Einsatz nach dem Download. Wer beispielsweise Architekten in Barcelona oder Restaurants in Paris als Leads nutzen kann, für den bieten diese Lösungen einen schnellen Zugang zu einer Menge an Daten.
Octoparse
Eine weitere Lösung, die ohne jede Programmierung und Vorkenntnis angewendet werden kann, um schnell große Mengen an Leads zu generieren. Dieses Programm hat eine besonders einfach zu bedienende Oberfläche und wurde direkt für die Leadgenerierung entwickelt.
80legs
Ebenfalls ein sehr nützliches Tool zum Web Scraping, mit dem man viele spezifische Einstellungen vornehmen kann. Zusätzlich bietet dieses Tool auch noch die Möglichkeit, die Daten sofort herunterzuladen. Es ist bestens geeignet um eine breite Basis an Leads zu generieren
Webharvy
Eine einfache Point-and-Click Software als Web Scraper, die einen URLs, E-Mail Adressen, Bilder und Texte von Webseiten sammeln kann. Auch dieses Tool lässt sich einfach ohne jede Programmierung intuitiv bedienen
Scraper
Eine Erweiterung für Google Chrome, die zwar nur begrenzte Daten sammeln kann, aber dennoch ein sehr hilfreiches Tool für die Onlinerecherche. Es ist geeignet für Beginner und Profis gleichermaßen, die Daten lassen sich bequem extrahieren und wie bei den anderen Programmen in eine .csv oder Ähnliche Datei verpacken.
com
Als open-source-basierter Cloud-Service für Webscraping handelt es sich hier um einen unabhängigen und hoch effektiven Web Scraper. Dadurch wird das Programm auch stetig upgedatet und verbessert. Die Software verwendet einen intelligenten Proxy Rotator, der darauf spezialisiert ist, die gängigen Maßnahmen gegen Bots auf Webseiten zu umgehen und trotz vorhandener Gegenmaßnahmen verlässlich die Daten zu sammeln. Sollte man Probleme mit dem Tool haben, steht ein zuverlässiges Support Team zur Verfügung, um bei Fragen zu helfen.
Fazit
Wer im Vertrieb arbeitet oder beispielsweise als Unternehmer auf einen starken, zuverlässigen Vertriebsprozess angewiesen ist, für den lässt sich das Thema Data Mining und Web Scraping heute nicht mehr länger ignorieren. Gerade in den noch “konservativen” Branchen, in denen nicht viel mit diesen digitalen Tools gearbeitet wird, lässt sich durch gekonnten Einsatz von Technologie ein Wettbewerbsvorteil erzeugen. Die Unternehmen, die gewillt sind sich auf diese neue Technologie einzulassen, können damit schneller und gezielter neue Kunden ansprechen und deren Produkte um ein Vielfaches effektiver vermarkten als jene Konkurrenten, die diese Tools nicht einsetzen.

 Datenbusiness
Datenbusiness





 Jurek Dörner @ DATANOMIQ
Jurek Dörner @ DATANOMIQ