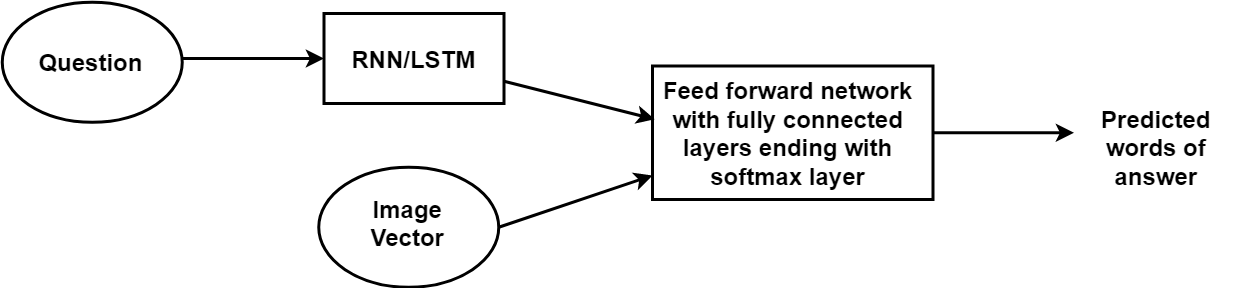
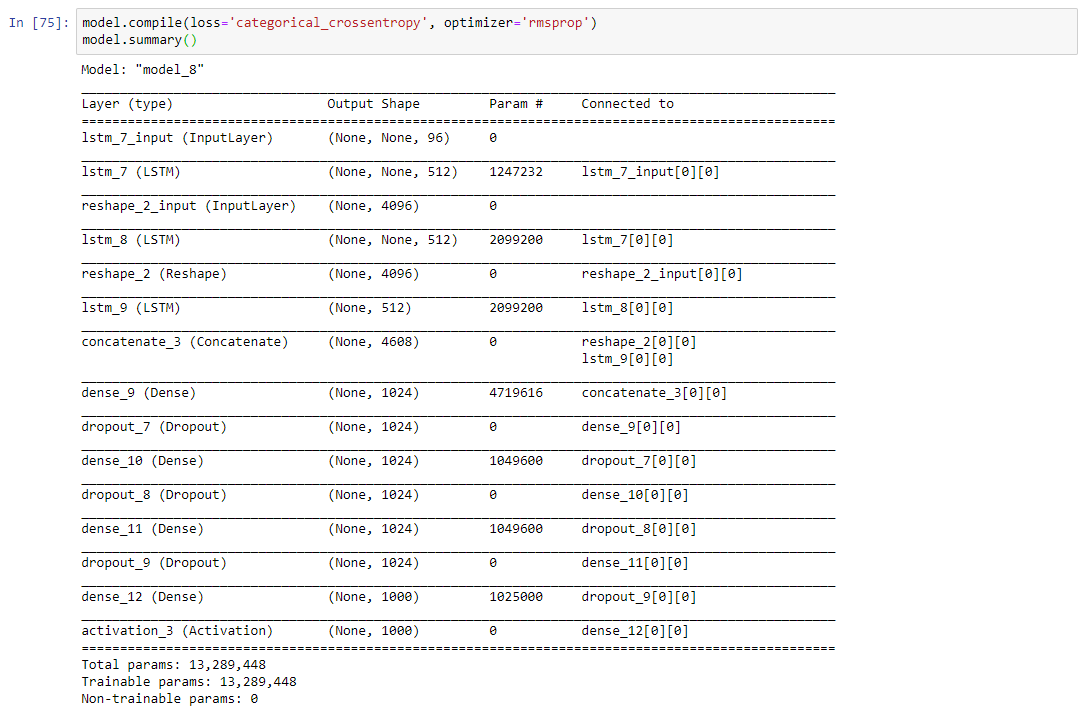
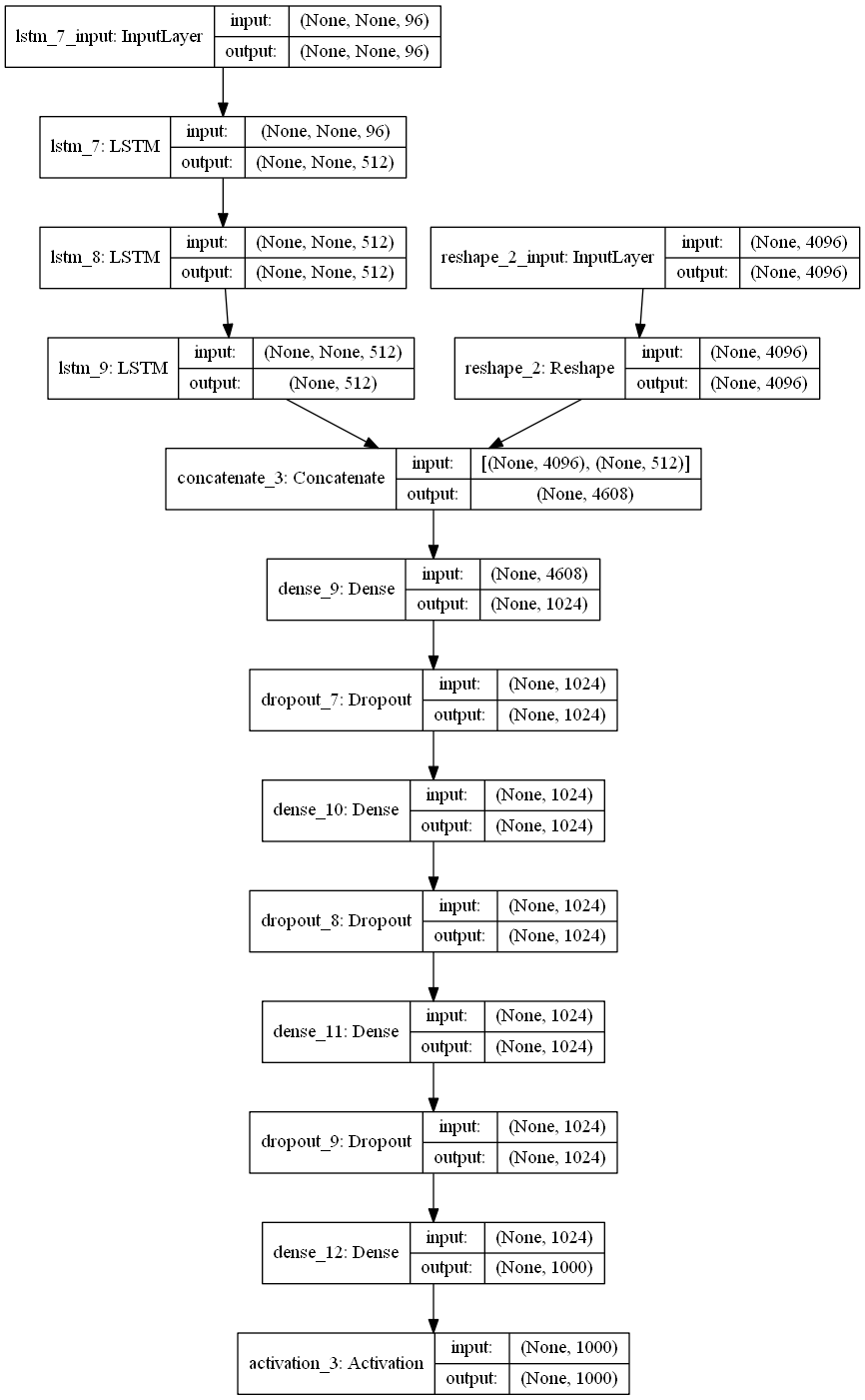
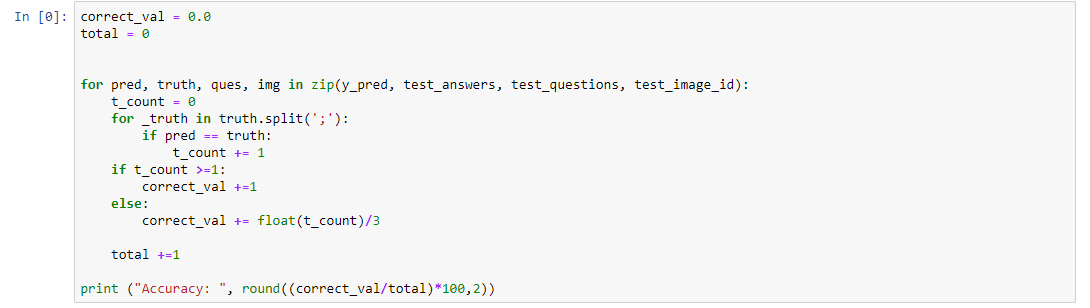
Healthcare industry is a recession-proof one. Even in times of economic meltdown and financial distress, the healthcare industry can hold its own because mankind will always need healthcare. In fact, during the Great Depression in the US, when the economy was facing a severe slowdown, the healthcare industry expanded, adding 852,000 jobs.
Healthcare AI in the US is slated to reach $6.6 billion in value by 2021.
From clinical trials to new drug research & development, and from innovative medical devices to technology like nanoparticles, AI, and ML has touched every point and has the power to transform them completely.
In fact, according to a study by Accenture, AI applications in healthcare can result in global savings to the tune of $150 billion by 2026.
The possibilities are endless, and the results unthinkable if AI can be properly used.
Here are some of the ways AI and ML can impact the healthcare industry:
1. Solving the Iron Triangle
A problem that has plagued the world for many years the triangle aims to solve a fundamental healthcare problem: that of good quality, accessible treatment at low cost.
Providing all three at the same time is a major challenge in healthcare, as the cost of healthcare is usually high. Here, trying to improve one factor harms another.
But AI can solve this problem in the near future without breaking the triangle, by improving the current healthcare cost-structure. The key to it is AI, and smart machines, that the patient can use for self-treatment for the majority of times, cutting down treatment costs drastically, by reducing human contact and improving quality of life.
2. Diagnostics and Imaging
The US FDA has drastically increased investment on AI in radiology and diagnostics. And it’s not without reason.
The IDx-DR became the first AI system cleared by the US FDA to provide diagnostic decisions. It was a breakthrough discovery to detect early mild diabetic retinopathy. The device was accurate 87.5% of the times, and also detected patients who didn’t have the condition, correctly up to 89.5% of times.
The US FDA also permitted marketing of the Viz.AI a type of clinical decision support system designed to analyze CT scan results to identify possibilities of a stroke in the patients and send the results to a specialist to identify any block.
In fact, diagnostics is fast becoming one of the significant drivers of AI investment in healthcare.
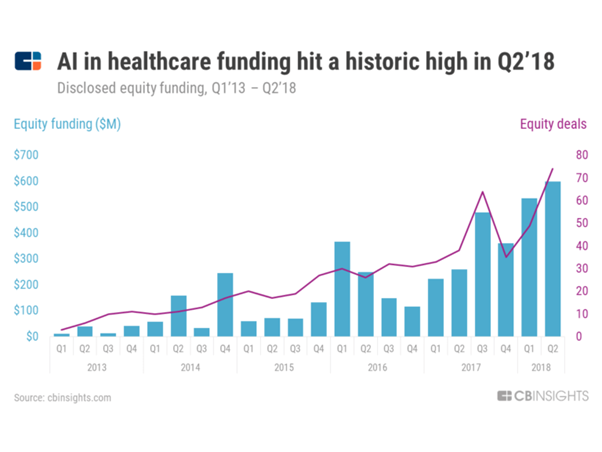
These advances can impact the healthcare industry in a novel way. As more and more devices become AI-enabled, the landscape of healthcare delivery will change.
3. Early screening
Early screening in case of most diseases can drastically improve the mortality rates of patients and cut down treatment costs by over 50%.
Let’s take the example of colorectal cancer.
The 5-year survival for Stage 1 CRC is around 90%, as compared to only 10% for Stage 4.
Early detection of CRC can be ideally treated with a minimally invasive endoscopy at a low cost of less than $5,000 per year. However, in the case of late-stage CRC, it requires multidisciplinary treatment with multiple surgeries, chemotherapy, and radiation, skyrocketing the costs.
And that is why early detection is essential, and that’s exactly what AI can do. There are already apps on the market that are doing this. For example, Autism & Beyond is a revolutionary app that leveraged the power of Apple’s ResearchKit to gather videos of children and detect their preference for the development of autism, using AI software.
AI used for early screening can save billions of taxpayer dollars of taxpayer money every year, and reduce out of pocket expenditure in the US drastically.
4. Drug research & development
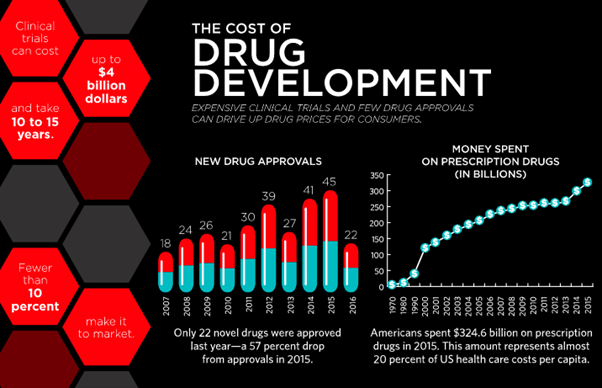
According to the California Biomedical Research Association, it takes around 12 years for a drug to be conceived in the laboratory and go to the patient.
Only 1 out of 5000 drugs that are selected for pre-clinical testing are then used for human testing, and only 20% of them make it to the market for human use.
(image)
The cost to develop a new drug now is more than $2.5 billion.
It is only recently that AI is being used in drug research and discovery. The power of AI can be leveraged to streamline the drug discovery and drug repurposing processes. It can identify patients best suited to the trial, can identify patients in the most need for new medications and can predict any side-effects and idiosyncrasies beforehand.
All of these, for a start, can lead to much safer clinical trials with no unwanted drug reactions.
And then, there is the question of lowering costs. In fact, a study by Carnegie Mellon and a German university estimated that AI could lower drug discovery costs by as much as 70%.
This, in turn, will be transferred to patients in the form of lower drug prices, which will increase accessibility to better medications for patients and improve population health in general.
5. Surgery
AI-enabled robotic-assisted surgeries are taking over the US. They are increasingly being used to reduce surgeon variations and improve quality.
‘Artificial intelligence can help surgeons perform better’ quotes Dr. John Birkmeyer, a chief clinical officer at Sound Physicians.
Advanced analytics and machine learning techniques are being used concomitantly used to unleash critical insights from the billions of data elements associated with robotic-assisted surgery. If used properly, this can help overcome attendant inefficiencies and improve patient health outcomes.
Artificial intelligence helps surgeons make better clinical decisions in real-time during surgery, and helps them understand the dynamics of the patient, especially during complex operations. It also reduces the length of stay of patients by 21%.
This is ultimately reflected in the patient’s post-operative care and long-term health. It also prevents patient readmissions, saving millions of dollars annually.
A study involving 379 orthopedic patients found out that AI-assisted robotic surgery resulted in five times fewer complications as compared to surgeons working alone.
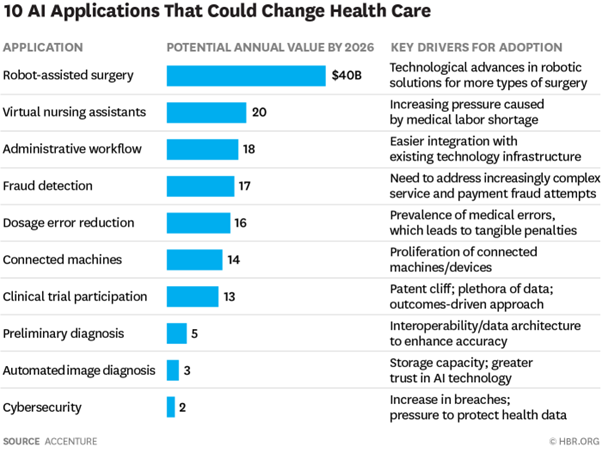
According to Accenture, AI-assisted robotic surgery could save the US healthcare industry $40 billion annually, by 2026.
6. AI-assisted virtual nurses
AI-assisted virtual nurses could well end up saving the US healthcare industry $20 billion annually, by 2026.
They are available 24/7 to answer any patient queries, monitor patients, and guide them in any way they might want.
Currently, they act as a bridge for information exchange between care providers (doctors) and care receivers (patients), to decide what medications to start, the current health status, the most recent test results, and many other things.
It can save the patient many physical appointments with doctors, and also prevent high hospital readmission rates through simple, engaging, and intelligent care.
Care Angel is one of the finest virtual nurses around. Apart from all of the above, it can also provide wellness checks through voice and AI.
Wrap-Up
AI and ML in healthcare are still at its infancy. Adoption at a large-scale is missing as of yet. To be successful in the healthcare domain, AI and ML need the endorsement of healthcare providers like physicians and nurses.
However, considerable investment is being made in AI in healthcare, and its increasing at a good rate.
AI in healthcare is currently aimed at improving patient outcomes, taking care of the interests of various stakeholders involved, increasing accessibility, and reducing healthcare costs.
In the near future, however, AI and ML, along with technologies like Data Science will take up a much more holistic role to drive healthcare forward.