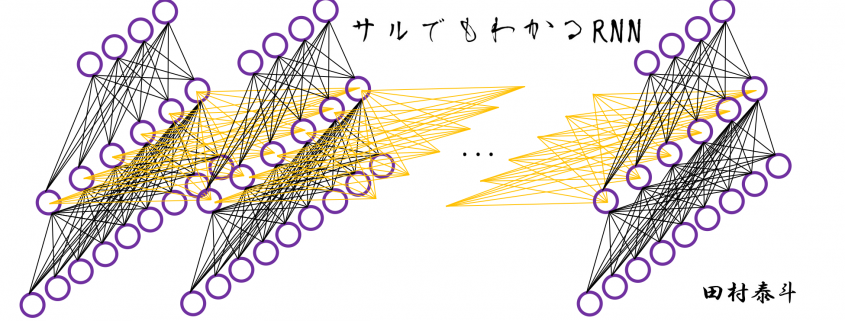
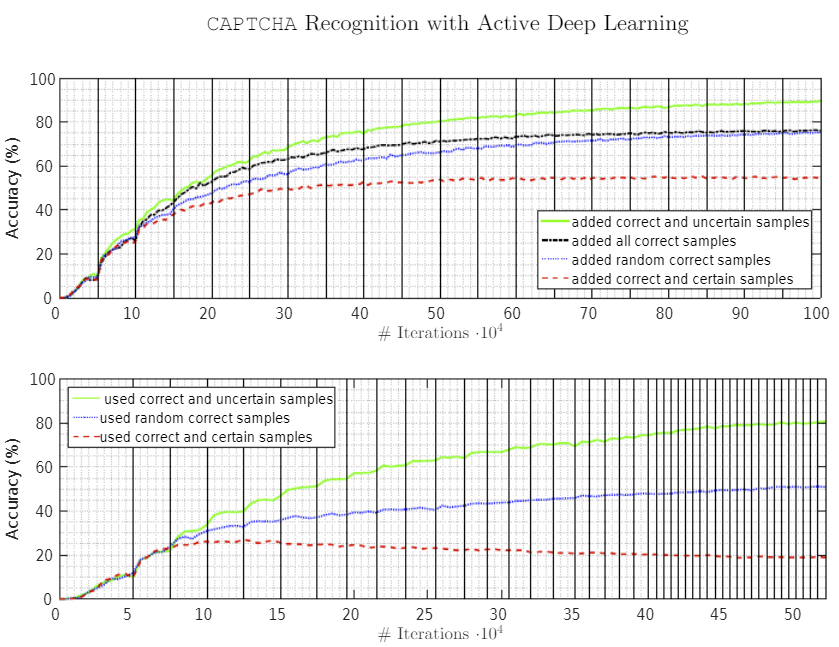
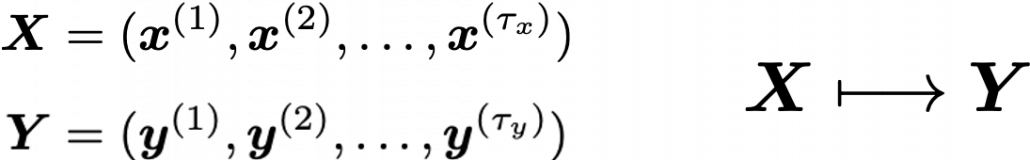Simple RNN: the first foothold for understanding LSTM
*In this article “Densely Connected Layers” is written as “DCL,” and “Convolutional Neural Network” as “CNN.”
In the last article, I mentioned “When it comes to the structure of RNN, many study materials try to avoid showing that RNNs are also connections of neurons, as well as DCL or CNN.” Even if you manage to understand DCL and CNN, you can be suddenly left behind once you try to understand RNN because it looks like a different field. In the second section of this article, I am going to provide a some helps for more abstract understandings of DCL/CNN , which you need when you read most other study materials.
My explanation on this simple RNN is based on a chapter in a textbook published by Massachusetts Institute of Technology, which is also recommended in some deep learning courses of Stanford University.
First of all, you should keep it in mind that simple RNN are not useful in many cases, mainly because of vanishing/exploding gradient problem, which I am going to explain in the next article. LSTM is one major type of RNN used for tackling those problems. But without clear understanding forward/back propagation of RNN, I think many people would get stuck when they try to understand how LSTM works, especially during its back propagation stage. If you have tried climbing the mountain of understanding LSTM, but found yourself having to retreat back to the foot, I suggest that you read through this article on simple RNNs. It should help you to gain a solid foothold, and you would be ready for trying to climb the mountain again.
*This article is the second article of “A gentle introduction to the tiresome part of understanding RNN.”
1, A brief review on back propagation of DCL.
Simple RNNs are straightforward applications of DCL, but if you do not even have any ideas on DCL forward/back propagation, you will not be able to understand this article. If you more or less understand how back propagation of DCL works, you can skip this first section.
Deep learning is a part of machine learning. And most importantly, whether it is classical machine learning or deep learning, adjusting parameters is what machine learning is all about. Parameters mean elements of functions except for variants. For example when you get a very simple function ![]() , then
, then ![]() is a variant, and
is a variant, and ![]() are parameters. In case of classical machine learning algorithms, the number of those parameters are very limited because they were originally designed manually. Such functions for classical machine learning is useful for features found by humans, after trial and errors(feature engineering is a field of finding such effective features, manually). You adjust those parameters based on how different the outputs(estimated outcome of classification/regression) are from supervising vectors(the data prepared to show ideal answers).
are parameters. In case of classical machine learning algorithms, the number of those parameters are very limited because they were originally designed manually. Such functions for classical machine learning is useful for features found by humans, after trial and errors(feature engineering is a field of finding such effective features, manually). You adjust those parameters based on how different the outputs(estimated outcome of classification/regression) are from supervising vectors(the data prepared to show ideal answers).
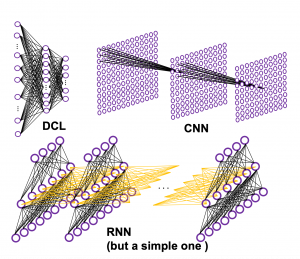
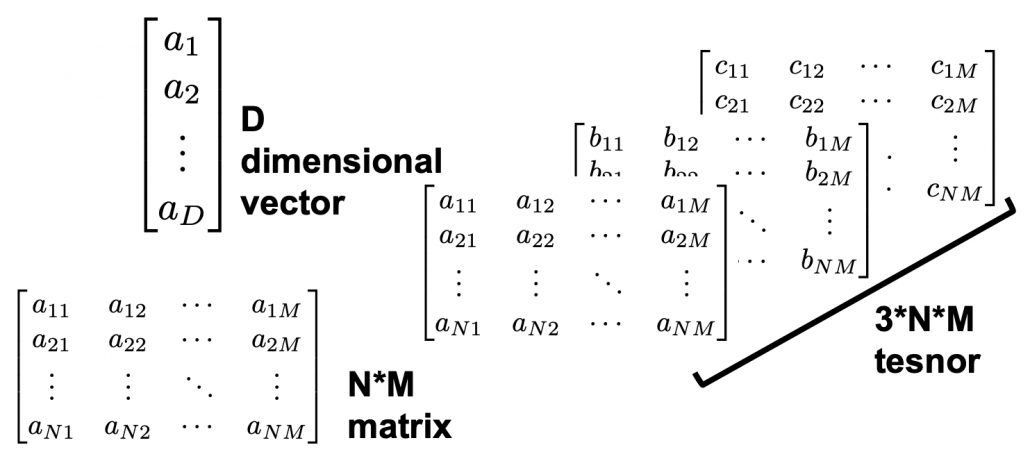
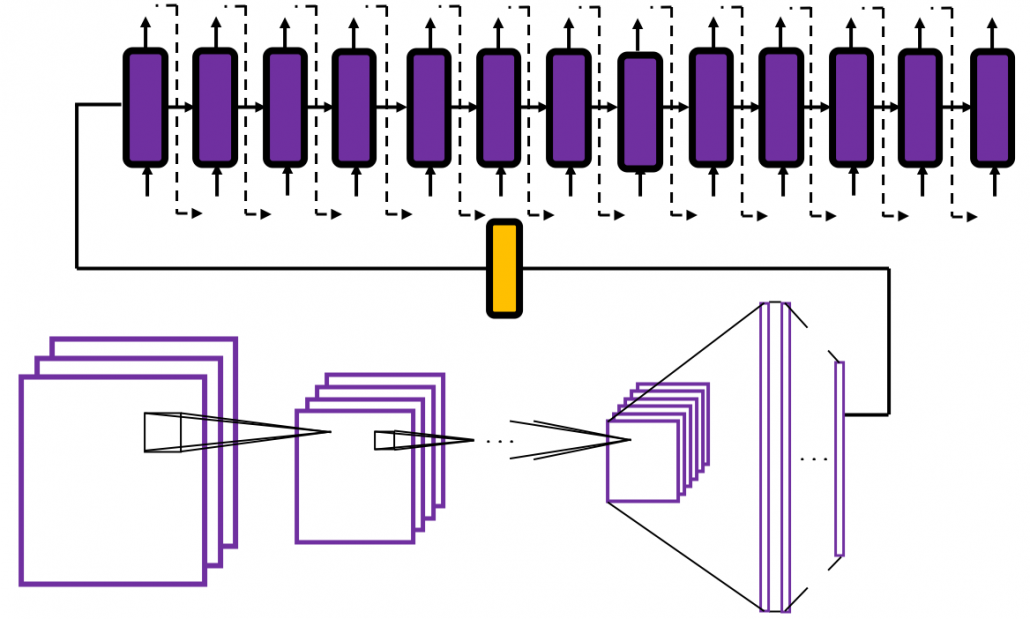
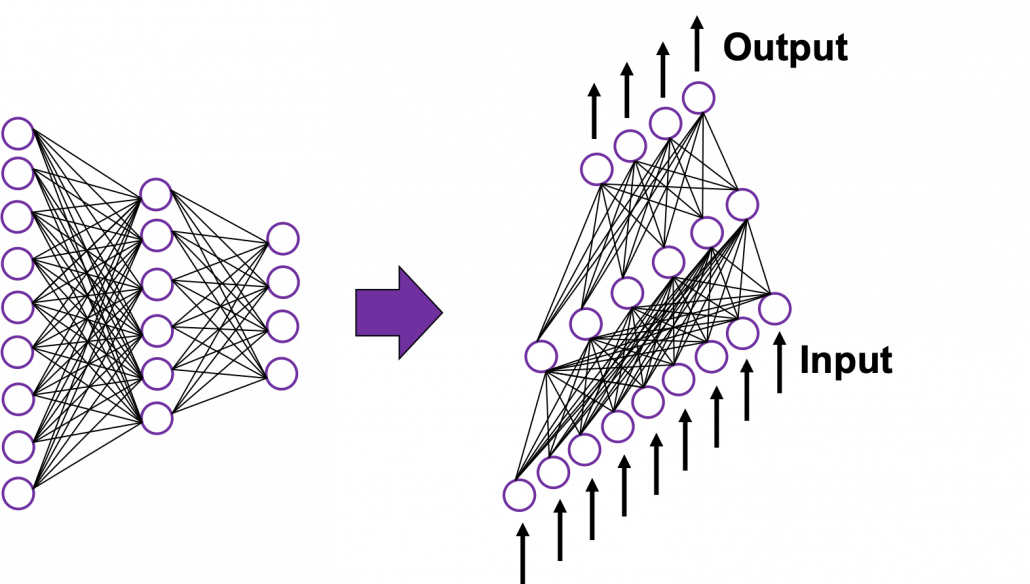
In the last article I said neural networks are just mappings, whose inputs are vectors, matrices, or sequence data. In case of DCLs, inputs are vectors. Then what’s the number of parameters ? The answer depends on the the number of neurons and layers. In the example of DCL at the right side, the number of the connections of the neurons is the number of parameters(Would you like to try to count them? At least I would say “No.”). Unlike classical machine learning you no longer need to do feature engineering, but instead you need to design networks effective for each task and adjust a lot of parameters.
*I think the hype of AI comes from the fact that neural networks find features automatically. But the reality is difficulty of feature engineering was just replaced by difficulty of designing proper neural networks.
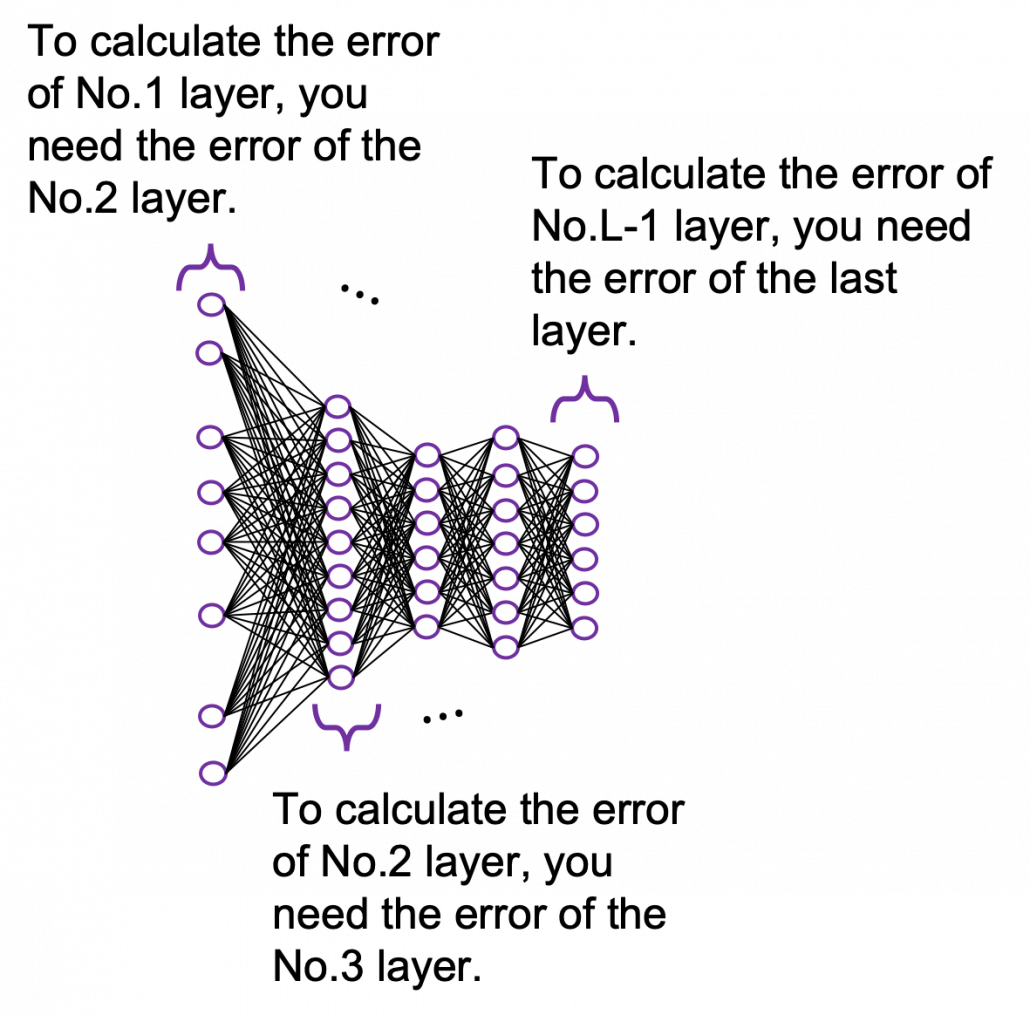
It is easy to imagine that you need an efficient way to adjust those parameters, and the method is called back propagation (or just backprop). As long as it is about DCL backprop, you can find a lot of well-made study materials on that, so I am not going to cover that topic precisely in this article series. Simply putting, during back propagation, in order to adjust parameters of a layer you need errors in the next layer. And in order calculate the errors of the next layer, you need errors in the next next layer.
*You should not think too much about what the “errors” exactly mean. Such “errors” are defined in this context, and you will see why you need them if you actually write down all the mathematical equations behind backprops of DCL.
The red arrows in the figure shows how errors of all the neurons in a layer propagate backward to a neuron in last layer. The figure shows only some sets of such errors propagating backward, but in practice you have to think about all the combinations of such red arrows in the whole back propagation(this link would give you some ideas on how DCLs work).
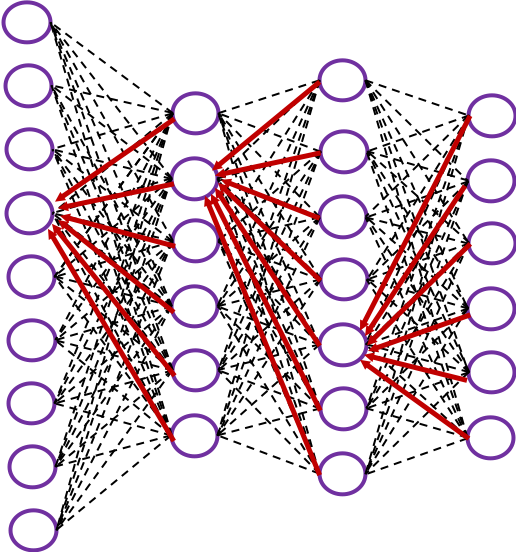
These points are minimum prerequisites for continuing reading this RNN this article. But if you are planning to understand RNN forward/back propagation at an abstract/mathematical level that you can read academic papers, I highly recommend you to actually write down all the equations of DCL backprop. And if possible you should try to implement backprop of three-layer DCL.
2, Forward propagation of simple RNN
*For better understandings of the second and third section, I recommend you to download an animated PowerPoint slide which I prepared. It should help you understand simple RNNs.
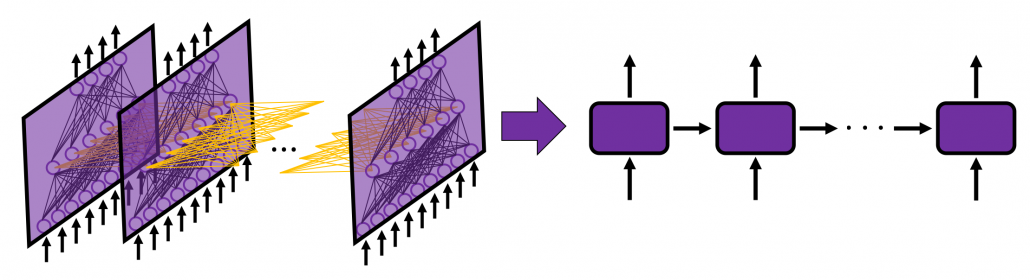
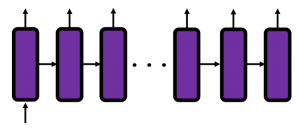
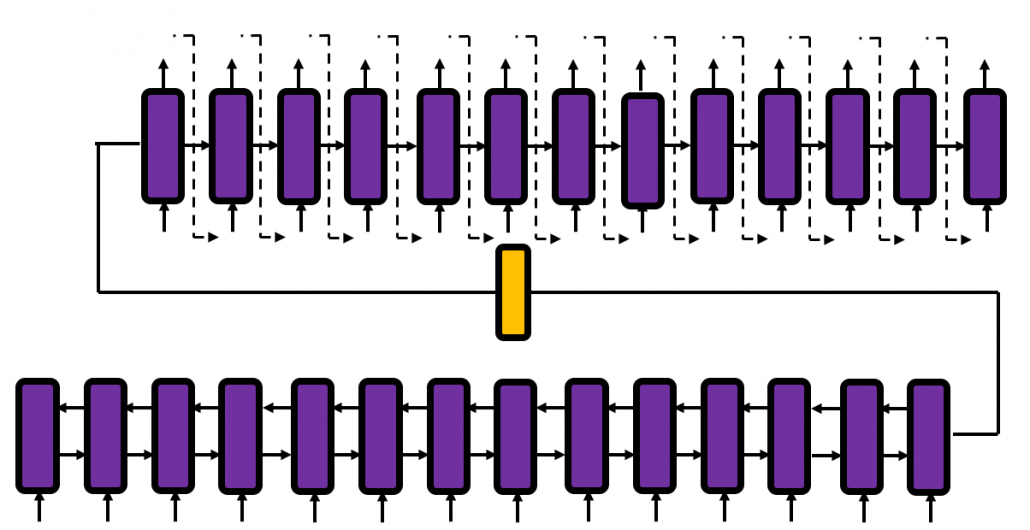
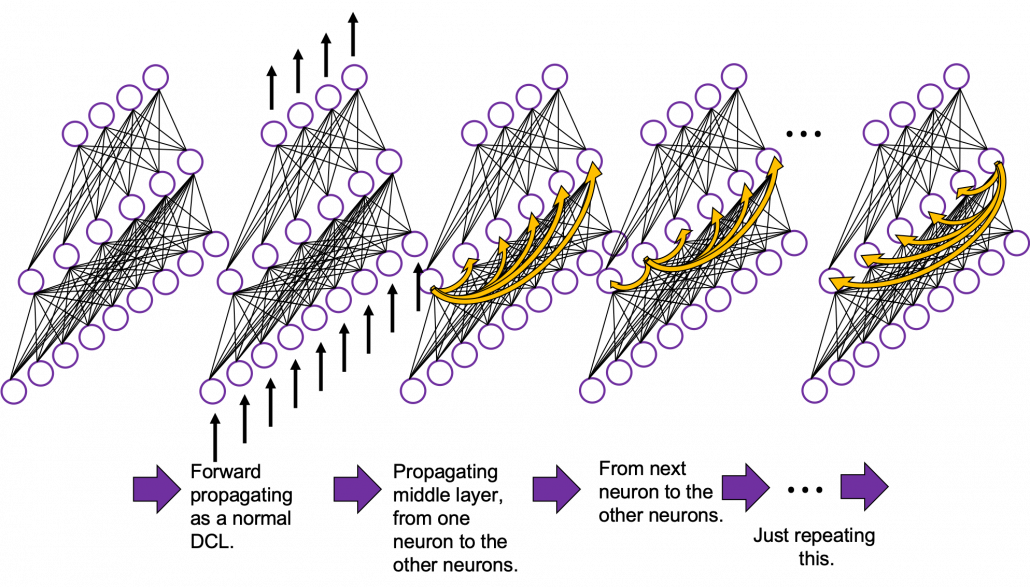
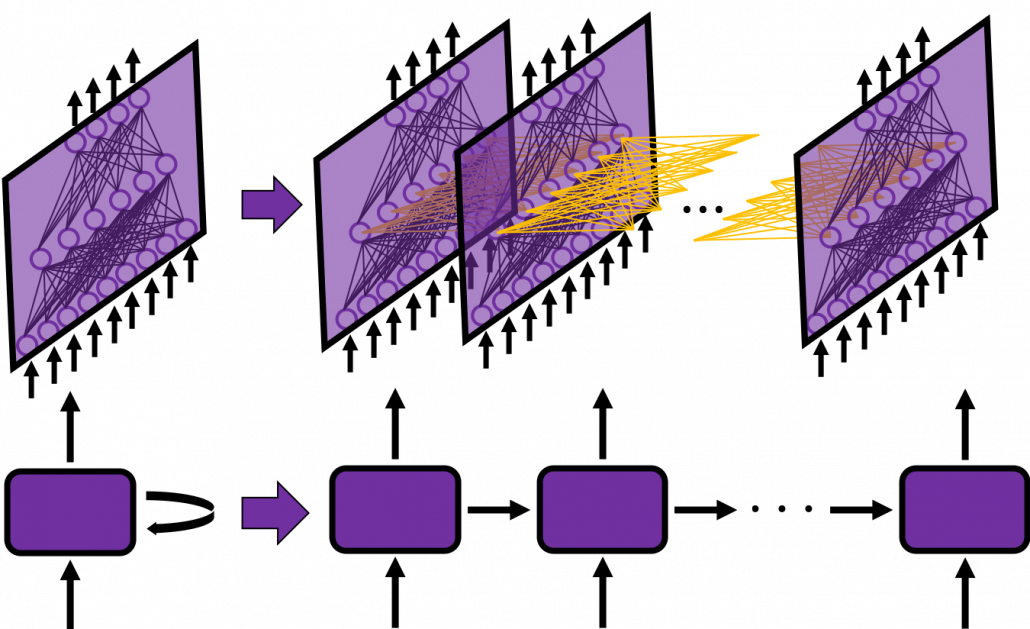
 In fact the simple RNN which we are going to look at in this article has only three layers. From now on imagine that inputs of RNN come from the bottom and outputs go up. But RNNs have to keep information of earlier times steps during upcoming several time steps because as I mentioned in the last article RNNs are used for sequence data, the order of whose elements is important. In order to do that, information of the neurons in the middle layer of RNN propagate forward to the middle layer itself. Therefore in one time step of forward propagation of RNN, the input at the time step propagates forward as normal DCL, and the RNN gives out an output at the time step. And information of one neuron in the middle layer propagate forward to the other neurons like yellow arrows in the figure. And the information in the next neuron propagate forward to the other neurons, and this process is repeated. This is called recurrent connections of RNN.
In fact the simple RNN which we are going to look at in this article has only three layers. From now on imagine that inputs of RNN come from the bottom and outputs go up. But RNNs have to keep information of earlier times steps during upcoming several time steps because as I mentioned in the last article RNNs are used for sequence data, the order of whose elements is important. In order to do that, information of the neurons in the middle layer of RNN propagate forward to the middle layer itself. Therefore in one time step of forward propagation of RNN, the input at the time step propagates forward as normal DCL, and the RNN gives out an output at the time step. And information of one neuron in the middle layer propagate forward to the other neurons like yellow arrows in the figure. And the information in the next neuron propagate forward to the other neurons, and this process is repeated. This is called recurrent connections of RNN.
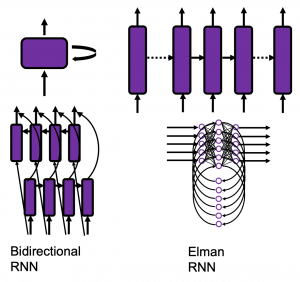
*To be exact we are just looking at a type of recurrent connections. For example Elman RNNs have simpler recurrent connections. And recurrent connections of LSTM are more complicated.
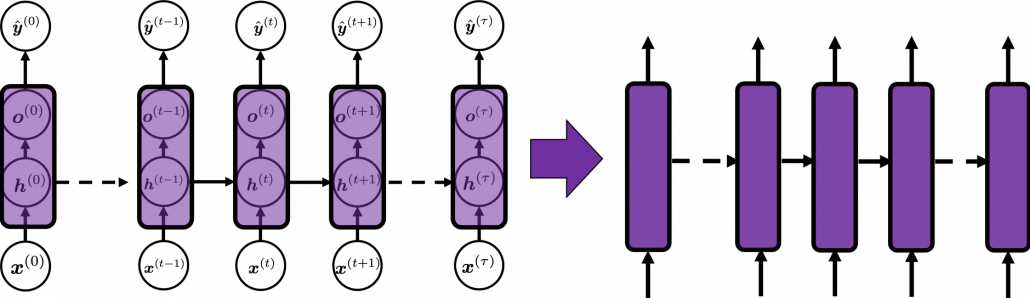
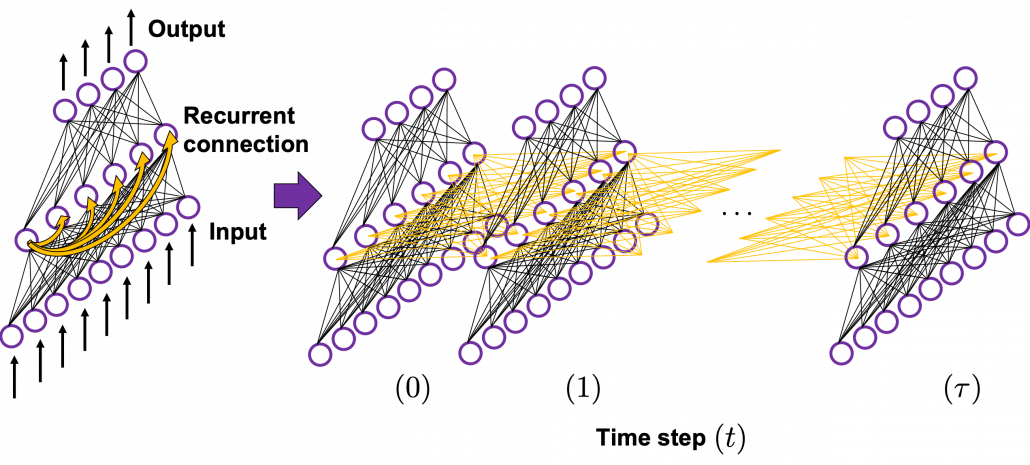
Whether it is a simple one or not, basically RNN repeats this process of getting an input at every time step, giving out an output, and making recurrent connections to the RNN itself. But you need to keep the values of activated neurons at every time step, so virtually you need to consider the same RNNs duplicated for several time steps like the figure below. This is the idea of unfolding RNN. Depending on contexts, the whole unfolded DCLs with recurrent connections is also called an RNN.
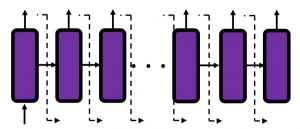
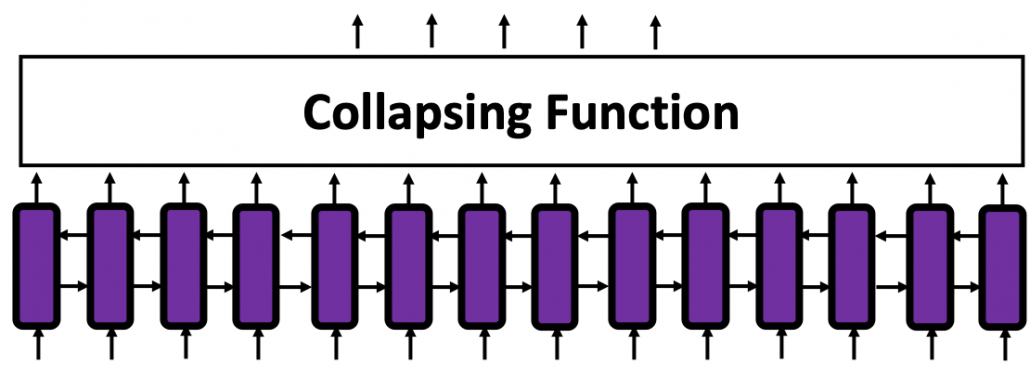
 In many situations, RNNs are simplified as below. If you have read through this article until this point, I bet you gained some better understanding of RNNs, so you should little by little get used to this more abstract, blackboxed way of showing RNN.
In many situations, RNNs are simplified as below. If you have read through this article until this point, I bet you gained some better understanding of RNNs, so you should little by little get used to this more abstract, blackboxed way of showing RNN.
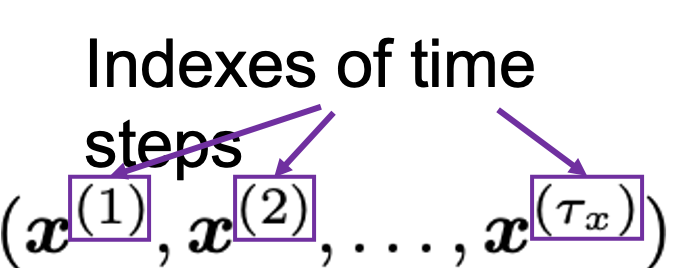
You have seen that you can unfold an RNN, per time step. From now on I am going to show the simple RNN in a simpler way, based on the MIT textbook which I recomment. The figure below shows how RNN propagate forward during two time steps ![]() .
.
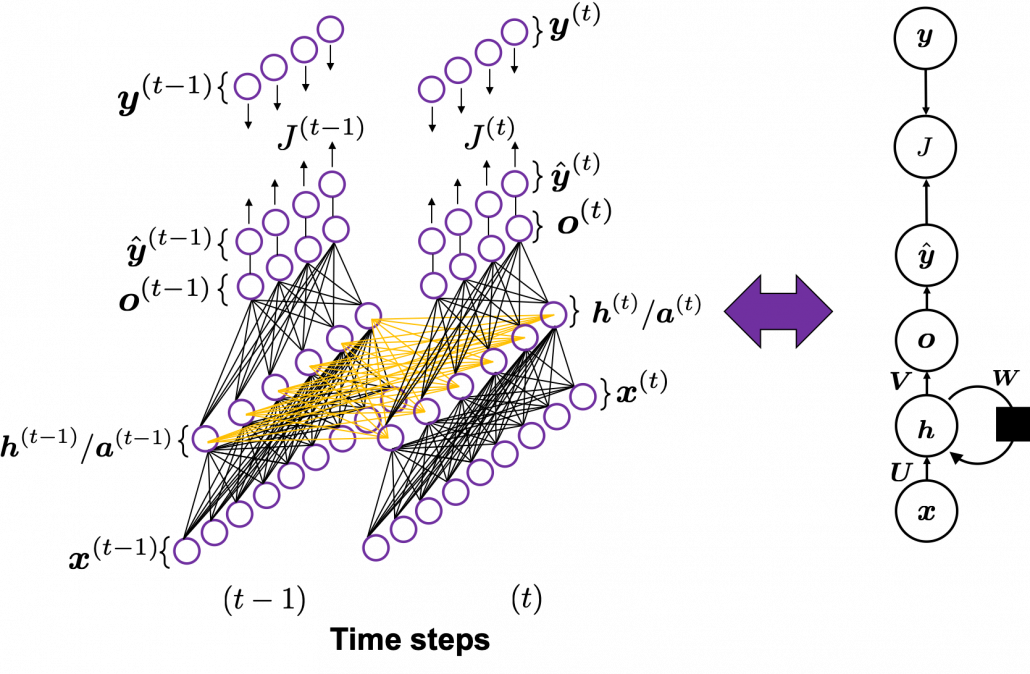
The input ![]() at time step
at time step![]() propagate forward as a normal DCL, and gives out the output
propagate forward as a normal DCL, and gives out the output ![]() (The notation on the
(The notation on the ![]() is called “hat,” and it means that the value is an estimated value. Whatever machine learning tasks you work on, the outputs of the functions are just estimations of ideal outcomes. You need to adjust parameters for better estimations. You should always be careful whether it is an actual value or an estimated value in the context of machine learning or statistics). But the most important parts are the middle layers.
is called “hat,” and it means that the value is an estimated value. Whatever machine learning tasks you work on, the outputs of the functions are just estimations of ideal outcomes. You need to adjust parameters for better estimations. You should always be careful whether it is an actual value or an estimated value in the context of machine learning or statistics). But the most important parts are the middle layers.
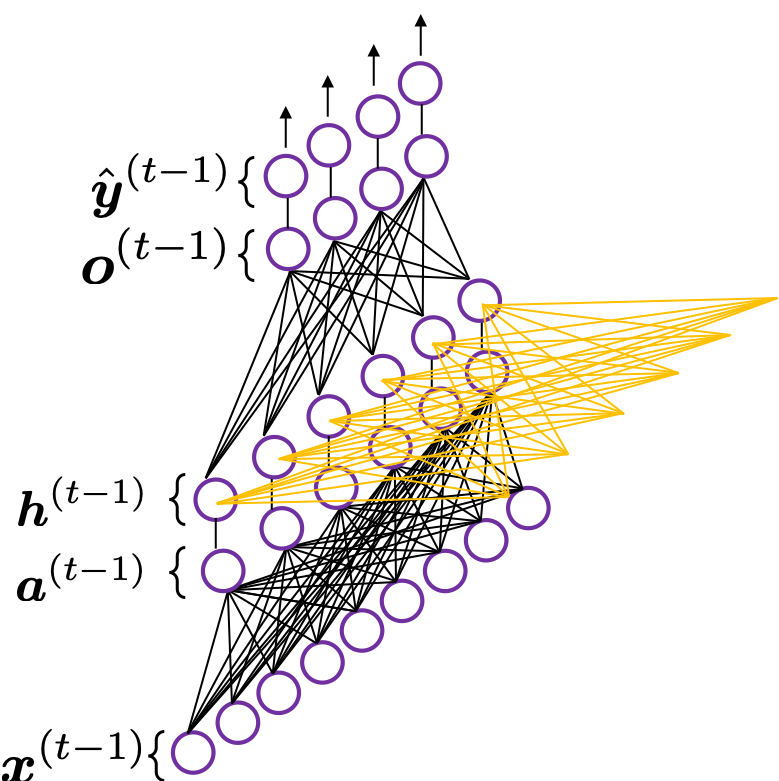
*To be exact I should have drawn the middle layers as connections of two layers of neurons like the figure at the right side. But I made my figure closer to the chart in the MIT textbook, and also most other study materials show the combinations of the two neurons before/after activation as one neuron.
![]() is just linear summations of
is just linear summations of ![]() (If you do not know what “linear summations” mean, please scroll this page a bit), and
(If you do not know what “linear summations” mean, please scroll this page a bit), and ![]() is a combination of activated values of
is a combination of activated values of ![]() and linear summations of
and linear summations of ![]() from the last time step, with recurrent connections. The values of
from the last time step, with recurrent connections. The values of ![]() propagate forward in two ways. One is normal DCL forward propagation to
propagate forward in two ways. One is normal DCL forward propagation to ![]() and
and ![]() , and the other is recurrent connections to
, and the other is recurrent connections to ![]() .
.
These are equations for each step of forward propagation.
*Please forgive me for adding some mathematical equations on this article even though I pledged not to in the first article. You can skip the them, but for some people it is on the contrary more confusing if there are no equations. In case you are allergic to mathematics, I prescribed some treatments below.
*Linear summation is a type of weighted summation of some elements. Concretely, when you have a vector ![]() , and weights
, and weights ![]() , then
, then ![]() is a linear summation of
is a linear summation of ![]() , and its weights are
, and its weights are ![]() .
.
*When you see a product of a matrix and a vector, for example a product of ![]() and
and ![]() , you should clearly make an image of connections between two layers of a neural network. You can also say each element of
, you should clearly make an image of connections between two layers of a neural network. You can also say each element of ![]() is a linear summations all the elements of
is a linear summations all the elements of ![]() , and
, and ![]() gives the weights for the summations.
gives the weights for the summations.

A very important point is that you share the same parameters, in this case ![]() , at every time step.
, at every time step.
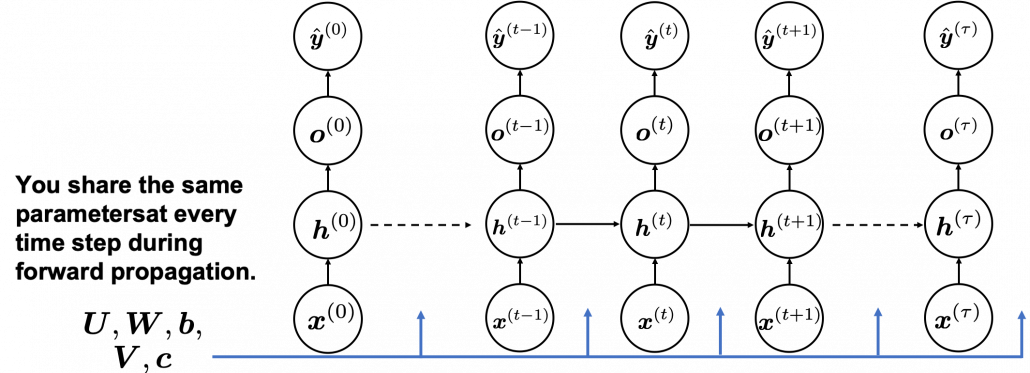
And you are likely to see this RNN in this blackboxed form.
3, The steps of back propagation of simple RNN
In the last article, I said “I have to say backprop of RNN, especially LSTM (a useful and mainstream type or RNN), is a monster of chain rules.” I did my best to make my PowerPoint on LSTM backprop straightforward. But looking at it again, the LSTM backprop part still looks like an electronic circuit, and it requires some patience from you to understand it. If you want to understand LSTM at a more mathematical level, understanding the flow of simple RNN backprop is indispensable, so I would like you to be patient while understanding this step (and you have to be even more patient while understanding LSTM backprop).
This might be a matter of my literacy, but explanations on RNN backprop are very frustrating for me in the points below.
- Most explanations just show how to calculate gradients at each time step.
- Most study materials are visually very poor.
- Most explanations just emphasize that “errors are back propagating through time,” using tons of arrows, but they lack concrete instructions on how actually you renew parameters with those errors.
If you can relate to the feelings I mentioned above, the instructions from now on could somewhat help you. And with the animated PowerPoint slide I prepared, you would have clear understandings on this topic at a more mathematical level.
Backprop of RNN , as long as you are thinking about simple RNNs, is not so different from that of DCLs. But you have to be careful about the meaning of errors in the context of RNN backprop. Back propagation through time (BPTT) is one of the major methods for RNN backprop, and I am sure most textbooks explain BPTT. But most study materials just emphasize that you need errors from all the time steps, and I think that is very misleading and confusing.
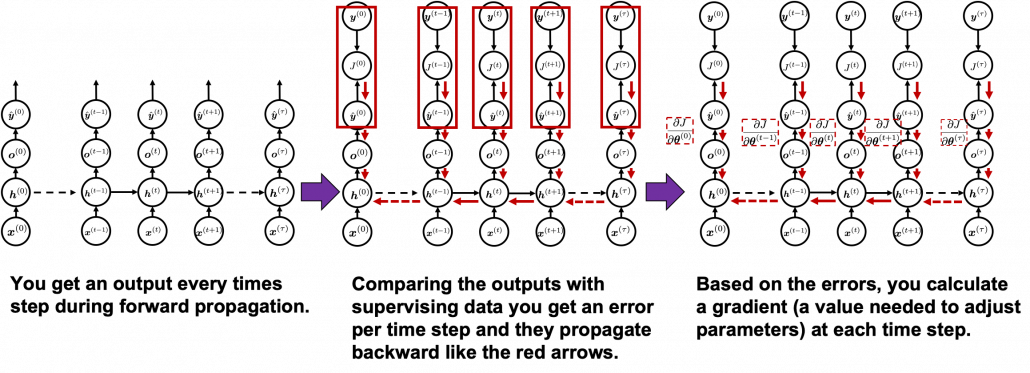 You need all the gradients to adjust parameters, but you do not necessarily need all the errors to calculate those gradients. Gradients in the context of machine learning mean partial derivatives of error functions (in this case
You need all the gradients to adjust parameters, but you do not necessarily need all the errors to calculate those gradients. Gradients in the context of machine learning mean partial derivatives of error functions (in this case ![]() ) with respect to certain parameters, and mathematically a gradient of
) with respect to certain parameters, and mathematically a gradient of ![]() with respect to
with respect to ![]() is denoted as
is denoted as ![]() . And another confusing point in many textbooks, including the MIT one, is that they give an impression that parameters depend on time steps. For example some study materials use notations like
. And another confusing point in many textbooks, including the MIT one, is that they give an impression that parameters depend on time steps. For example some study materials use notations like ![]() , and I think this gives an impression that this is a gradient with respect to the parameters at time step
, and I think this gives an impression that this is a gradient with respect to the parameters at time step ![]() . In my opinion this gradient rather should be written as
. In my opinion this gradient rather should be written as ![]() . But many study materials denote gradients of those errors in the former way, so from now on let me use the notations which you can see in the figures in this article.
. But many study materials denote gradients of those errors in the former way, so from now on let me use the notations which you can see in the figures in this article.
In order to calculate the gradient ![]() you need errors from time steps
you need errors from time steps ![]() (as you can see in the figure, in order to calculate a gradient in a colored frame, you need all the errors in the same color).
(as you can see in the figure, in order to calculate a gradient in a colored frame, you need all the errors in the same color).
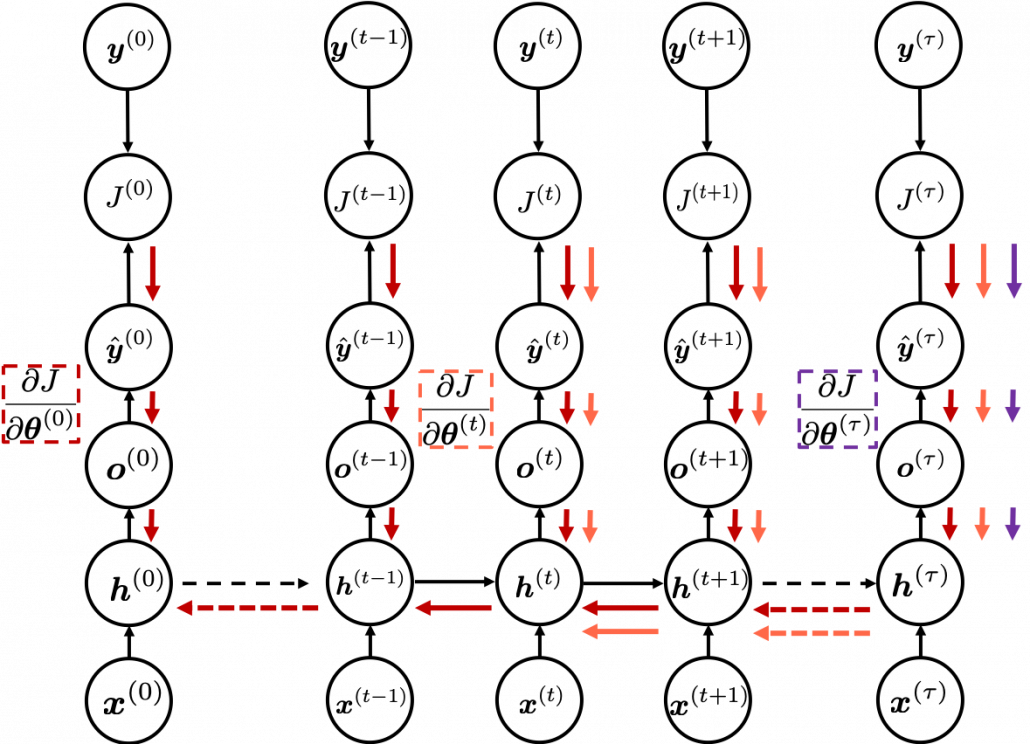
*To be exact, in the figure above I am supposed prepare much more arrows in ![]() different colors to show the whole process of RNN backprop, but that is not realistic. In the figure I displayed only the flows of errors necessary for calculating each gradient at time step
different colors to show the whole process of RNN backprop, but that is not realistic. In the figure I displayed only the flows of errors necessary for calculating each gradient at time step ![]() .
.
*Another confusing point is that the ![]() are correct notations, because
are correct notations, because ![]() are values of neurons after forward propagation. They depend on time steps, and these are very values which I have been calling “errors.” That is why parameters do not depend on time steps, whereas errors depend on time steps.
are values of neurons after forward propagation. They depend on time steps, and these are very values which I have been calling “errors.” That is why parameters do not depend on time steps, whereas errors depend on time steps.
As I mentioned before, you share the same parameters at every time step. Again, please do not assume that parameters are different from time step to time step. It is gradients/errors (you need errors to calculate gradients) which depend on time step. And after calculating errors at every time step, you can finally adjust parameters one time, and that’s why this is called “back propagation through time.” (It is easy to imagine that this method can be very inefficient. If the input is the whole text on a Wikipedia link, you need to input all the sentences in the Wikipedia text to renew parameters one time. To solve this problem there is a backprop method named “truncated BPTT,” with which you renew parameters based on a part of a text. )
And after calculating those gradients ![]() you can take a summation of them:
you can take a summation of them: ![]() . With this gradient
. With this gradient ![]() , you can finally renew the value of
, you can finally renew the value of ![]() one time.
one time.
At the beginning of this article I mentioned that simple RNNs are no longer for practical uses, and that comes from exploding/vanishing problem of RNN. This problem was one of the reasons for the AI winter which lasted for some 20 years. In the next article I am going to write about LSTM, a fancier type of RNN, in the context of a history of neural network history.
* I make study materials on machine learning, sponsored by DATANOMIQ. I do my best to make my content as straightforward but as precise as possible. I include all of my reference sources. If you notice any mistakes in my materials, including grammatical errors, please let me know (email: yasuto.tamura@datanomiq.de). And if you have any advice for making my materials more understandable to learners, I would appreciate hearing it.