Fraud has the potential to shatter businesses of all sizes and in all industries. Now that many businesses operate online at least partially, if not completely, the fraud risks are more prominent than ever. Right alongside the perks of reaching an enormous audience and using endless marketing tricks for promotion, businesses have to find a way to mitigate such risks.
One global economic crime survey, from PwC, found that 47% of all businesses worldwide experienced some type of fraud in the last 2 years. While online sales are higher than ever and are expected to grow significantly, this is all matched by a growth in fraud.
If we stop to take a look at how the eCommerce world has progressed in just a few years, the risks are becoming more imminent. Nowadays, it is more important than ever to take action to mitigate risks.
These days, online retailers deal with approximately 206,000 attacks on their businesses each month, research shows. Cybercriminals keep looking – and finding – new ways to capture and use data obtained from businesses, something that can ruin the brand entirely.
If you operate your business online, it is your obligation to your customers and your company to protect if from fraudsters that will steal data and wreck your online reputation. A single instance of fraud can alienate many of your customers and damage your brand, often without any chance to fix it.
Your job is to continuously track the trends, know the risks, and practice data science security hacks to mitigate fraud risks. In this article, you’ll learn all about it. But first, let’s take a look at why fraud happens in the first place.
Why does online fraud take place?
There are two big reasons why fraudsters can get access to data on your website and ruin your business:
- It is easy. Before the Internet existed and businesses were solely physical, fraudsters needed to do things like rob the place or steal physical cards to make purchases with. These days, fraudsters use their hacking skills to buy cards and make purchases, get access to customer data on your website, etc.
- It’s often conducted anonymously. Scamming online stores gives fraudsters a high sense of anonymity. They cannot be caught on camera and they can operate from any location in the world. Most police departments don’t make this a priority, so most of them remain uncaught, while businesses suffer the consequences.
Unless you take precautions to prevent this from happening, you are opening your company to many fraud risks. The good thing is, you can actually take precautions and measures to prevent and minimize the effects of fraud when it happens.
How to mitigate fraud risks for your online business
Now that you know how frequently this happens – and why that is the case, it’s time to go through some actionable tips on how to minimize the risks.
1. Use quality tools for modern fraud monitoring
Did you know that you can use tools to monitor and prevent fraud? Modern tools that are rich with features can protect your business’ data, as well as protect it from risky transactions. If you take a look at this guide on modern fraud monitoring, from SEON, a top-rated tool used for this purpose, you’ll find that there’s a lot to be done to mitigate such risks.
Some of the key features to benefit from when it comes to such tools are:
- Real-time monitoring – at all times
- Behavior tracking
- Fraud scoring
- Graph visualization
- Risk-based authentication
- Manual queries
- Alerts and reporting
- Sandboxing capacity
Thankfully, SEON has all that and more. Thanks to SEON, businesses can now authenticate their customers, automatically cancel or detect risky orders, block visitors based on geolocation, and create a variety of custom filters based on their preferences.
2. Know your fraud risks
It’s impossible to prevent something that you don’t know anything about. Many companies aren’t even aware of the risks before they actually happen. When they realize it, the damage is already done.
Let’s go through the main types of fraud risks that you should work to mitigate today:
This type of fraud is a banking data crime. It’s a big term that includes all sorts of stealing and illegally using credit card information. In some cases, criminals will use stolen credit card information to buy services or products on your website.
In more severe cases, they’ll be able to get this from your website, which means that you aren’t keeping your customer’s payment details safe enough.
Either way, you are looking at grand losses and problems. Eventually, when people use stolen cards, this defrauds the business owners that have to refund the purchase.
Chargeback fraud happens when a credit card provider asks the retailer to refund a disputed or fraudulent transaction. This happens when people buy a product or a service, receive it, but then request a full refund from the company that provided them with the card. It is also known as friendly fraud. In most cases, criminals wait a few weeks or even a few months after receiving the goods, and then contact the bank to dispute a transaction ‘they don’t know happened’. Some merchants are too busy to notice this, so they are losing tons of money because of it.
Affiliate fraud is done when criminals use fake data to generate affiliate commissions. In the affiliate marketing world, online businesses pay affiliates commission for clicks or sales they refer to the website. Criminals often game these systems and make it seem like there’s real activity to generate commissions or increase their amount.
This is one of the gravest and yet, most common frauds for online businesses. Most online businesses today provide their customers with accounts to facilitate their purchasing process and track their behaviors. This is where financial data, personal information, and purchase history are all stored. Through phishing schemes, fraudsters obtain this personal data, log into the accounts, and make unauthorized purchases.
These are just a few types of eCommerce fraud that occurs online. If you want to prevent them, you need to learn what your business is at risk for, and use the necessary tools to mitigate those risks.
3. Audit your website regularly
Your website is your storefront and it is one of the most important things to work on. You shouldn’t just work on its design or the content you publish on it. If you want to discover flaws in it before fraudsters do and use it to their benefit, you need to audit it carefully – and regularly.
Using fraud detection tools is a great step toward this, but you should also make sure to check some other things, too.
For example, are your shopping cart plugins and software up-to-date?
Do you have a working SSL certificate or is it expired?
Does your site comply with the current data protection laws and regulations?
Is your store Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) compliant?
Do you back it up as often as you should?
Have you updated your passwords recently, your hosting dashboard, and your CMS database?
4. Pay close attention to high-value orders
Small frauds can cost you a bit of money and a bit of your reputation. Big frauds can kill your business and your reputation in the industry. This is why you should pay close attention to high-value orders before shipping them out.
Check these personally, even the gift cards. Such items are very often used by fraudsters who hope to resell them, but have obtained them illegally.
5. Don’t be afraid to contact your customers
Customers that buy from you regularly will have similar behaviors every time they make a purchase. Your system will start flagging any unexpected behavior on their behalf. When that happens and you notice that an existing customer changed their patterns dramatically, don’t be afraid to reach out to them. This might save them and you a lot of money and keep them safer. Not to mention, it will make your brand even more trustworthy and secure in their eyes.
6. Request the CVV number for purchases
The back of cards such as Visa, MasterCard, and Discover contains a three-digit security code called the Card Verification Value or CVV. American Express cards have a four-digit code on the back.
Why is it smart to request this number?
Most fraudsters have the card numbers and expiry date but don’t have the CVV. This will minimize the risks and make it impossible for them to make fraudulent purchases if they don’t have the physical card on them.
7. Limit the amount of customer data you are collecting
It can be tempting to collect tons of customer data, especially for research. You can use this data to improve your marketing strategies and your brand and offer customers a more personalized experience. But, collecting a lot of data means that you are creating more risks for that data to be stolen.
That being said, make it your mission to collect and store as little data as possible. Collect only what is necessary.
Are you already doing these things?
Fraudsters are getting smarter about how they attack online businesses. It is your obligation to keep up with the scams in the digital world and find ways to mitigate the risks. This article gives you seven excellent starting points for this.

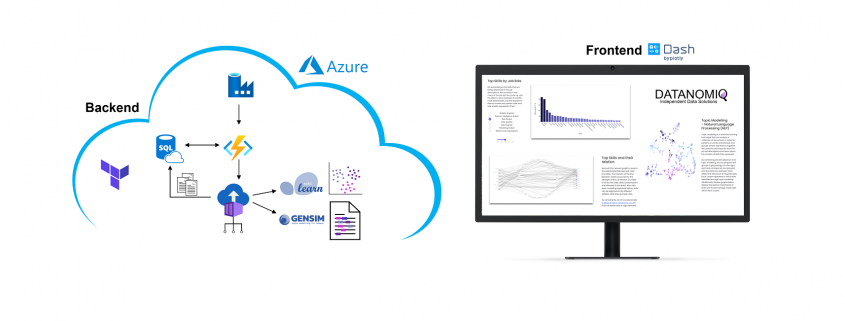
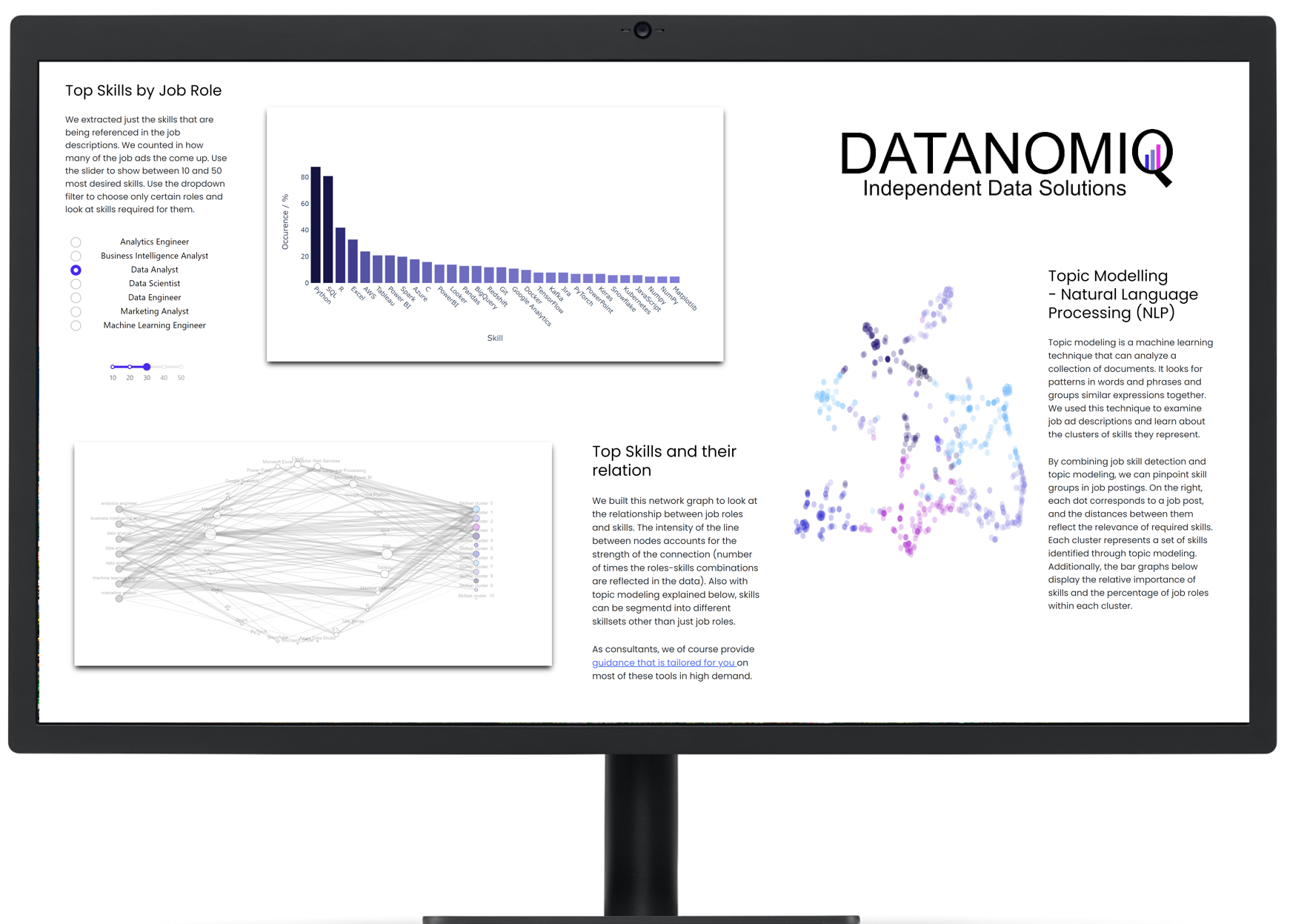


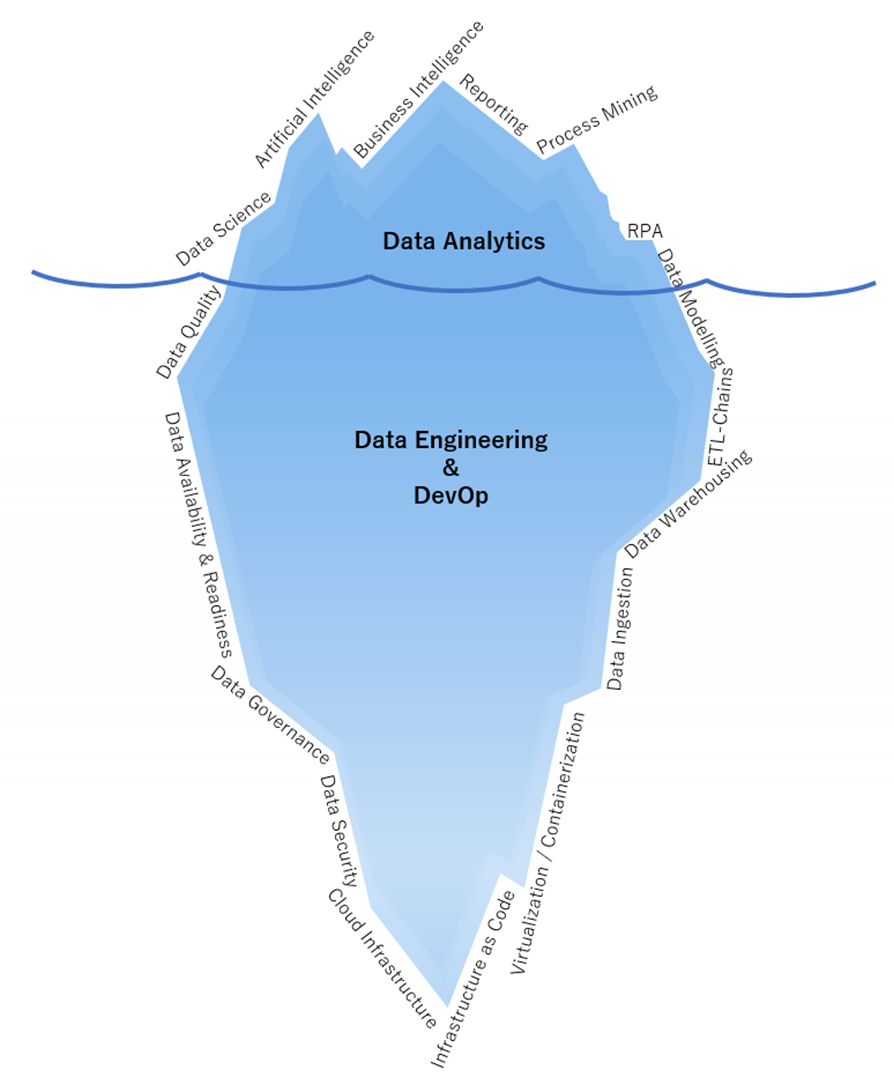
 DATANOMIQ is the independent consulting and service partner for business intelligence, process mining and data science. We are opening up the diverse possibilities offered by big data and artificial intelligence in all areas of the value chain. We rely on the best minds and the most comprehensive method and technology portfolio for the use of data for business optimization.
DATANOMIQ is the independent consulting and service partner for business intelligence, process mining and data science. We are opening up the diverse possibilities offered by big data and artificial intelligence in all areas of the value chain. We rely on the best minds and the most comprehensive method and technology portfolio for the use of data for business optimization.