process.science presents a new release
Advertisement
Process Mining Tool provider process.science presents a new release
process.science, specialist in the development of process mining plugins for BI systems, presents its upgraded version of their product ps4pbi. Process.science has added the following improvements to their plug-in for Microsoft Power BI. Identcal upgrades will soon also be released for ps4qlk, the corresponding plug-in for Qlik Sense:
- 3x faster performance: By improvement of the graph library the graph built got approx. 300% more performant. This is particularly noticeable in complex processes
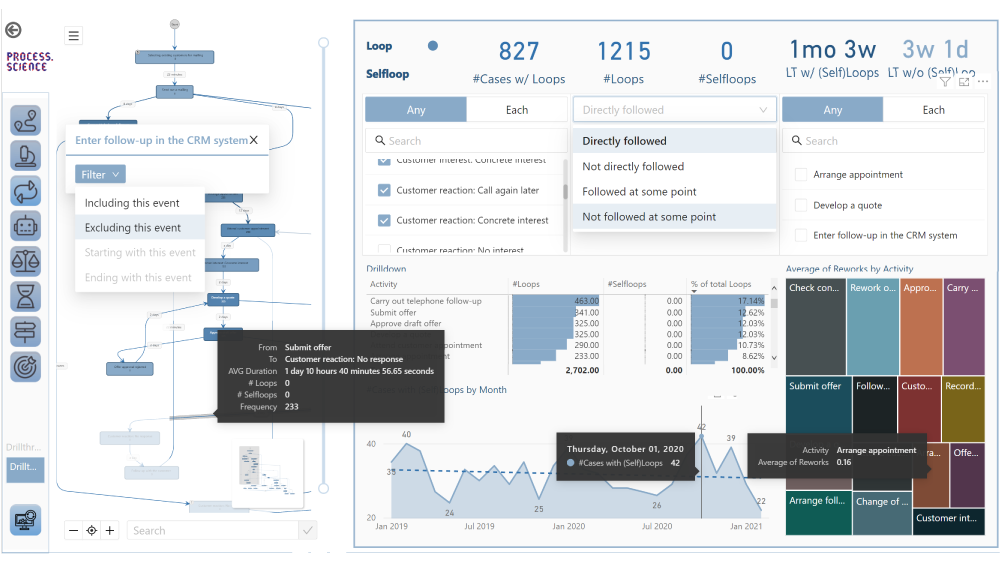
- Navigator window: For a better overview in complex graphs, an overview window has been added, in which the entire graph and the respective position of the viewed area within the overall process is displayed
- Activities legend: This allows activities to be assigned to specific categories and highlighted in different colors, for example in which source system an activity was carried out
- Activity drill-through: This makes it possible to take filters that have been set for selected activities into other dashboards
- Value Color Scale: Activity values can be color-coded and assigned to freely selectable groupings, which makes the overview easier at first sight
process.science Process Mining on Power BI
Process mining is a business data analysis technique. The software used for this extracts the data that is already available in the source systems and visualizes them in a process graph. The aim is to ensure continuous monitoring in real time in order to identify optimization measures for processes, to simulate them and to continuously evaluate them after implementation.
The process mining tools from process.science are integrated directly into Microsoft Power BI and Qlik Sense. A corresponding plug-in for Tableau is already in development. So it is not a complicated isolated solution requires a new set up in addition to existing systems. With process.science the existing know-how on the BI system already implemented and the existing infrastructure framework can be adapted.
The integration of process.science in the BI systems has no influence on day-to-day business and bears absolutely no risk of system failures, as process.science does not intervene in the the source system or any other program but extends the respective business intelligence tool by the process perspective including various functionalities.
Contact person for inquiries:
process.science GmbH & Co. KG
Gordon Arnemann
Tel .: + 49 (231) 5869 2868
Email: ga@process.science
https://de.process.science/